In a world where innovation drives progress, Tesla stands at the forefront of transforming transportation with its bold Robotaxi initiative. This revolutionary concept is not just about cars driving themselves; it’s about reshaping how people view and interact with urban mobility. From tech enthusiasts to environmentalists, the Tesla Robotaxi promises to offer something for everyone. But what exactly is a Tesla Robotaxi? And why is it such a game-changer?

Introduction to Tesla Robotaxi
Tesla’s Robotaxi isn’t just another autonomous vehicle—it’s a vision of the future. At its core, the concept involves self-driving Teslas operating as on-demand ride-sharing vehicles, eliminating the need for human drivers. This innovation marks a significant step forward in both the automotive and technology sectors, promising to alter how cities function and how individuals commute.
For Tesla, the Robotaxi represents a synthesis of their cutting-edge technology, environmental mission, and ambition to revolutionize transportation networks. It’s a project that highlights the company’s drive to push boundaries and explore new horizons in mobility. For tech enthusiasts and investors, understanding this initiative is crucial to grasping the full scope of Tesla’s innovation prowess.
Understanding Tesla’s Approach
The development of Tesla’s Robotaxi is deeply rooted in the company’s long-term vision for autonomous driving. Tesla’s approach leverages its existing vehicles equipped with Full Self-Driving (FSD) software, an advanced suite capable of navigating complex urban environments without human intervention. This technology underpins the Robotaxi network, creating a seamless blend of automotive excellence and artificial intelligence.

Tesla’s massive infrastructure investments, including its vast network of Superchargers and strategically positioned service centers, provide the backbone for the Robotaxi fleet. These resources ensure that the Robotaxi service can operate efficiently, minimizing downtime and maximizing accessibility for users across urban landscapes.
Central to Tesla’s strategy is the integration of its vehicles into a shared network, allowing owners to add their cars to the Robotaxi fleet when not in use. This not only maximizes the utility of each vehicle but also offers potential financial incentives for Tesla owners, encouraging widespread adoption and participation in this groundbreaking venture.
The Impact on Urban Commuting and Ride-Sharing
The introduction of Tesla’s Robotaxi service promises to revolutionize urban commuting, offering a convenient, cost-effective alternative to traditional ride-sharing options. By enabling cars to autonomously ferry passengers, Tesla aims to reduce traffic congestion, decrease travel times, and enhance the overall efficiency of urban transportation systems.
For ride-sharing users, Tesla’s Robotaxi presents a compelling proposition—access to state-of-the-art electric vehicles with autonomous capabilities. This service could democratize access to premium vehicles, providing a luxurious travel experience at a fraction of the cost associated with traditional car ownership or ride-hailing services.
Furthermore, the widespread deployment of Robotaxis could encourage the transformation of cityscapes, as reduced car ownership leads to a decrease in the demand for parking spaces and infrastructure. Urban planners may find new opportunities to repurpose land for green spaces, bike lanes, and pedestrian pathways, fostering healthier, more sustainable living environments.
The Potential for Investors and Businesses
For investors, Tesla’s Robotaxi initiative presents a tantalizing opportunity to tap into a burgeoning market poised for exponential growth. With autonomous ride-sharing projected to become a multi-billion-dollar industry, Tesla’s first-mover advantage positions it as a key player in this space, offering substantial returns for investors who recognize the potential.
Businesses, too, stand to benefit from the widespread adoption of Robotaxis. Corporate fleets could be integrated into Tesla’s network, optimizing logistics and reducing operational costs. Additionally, the data generated from autonomous operations could provide valuable insights for companies looking to enhance their market strategies and stay ahead of competitors.
The Robotaxi initiative has the potential to create new partnerships and collaborations between Tesla and various stakeholders, ranging from tech startups to urban mobility firms. This synergy could spur innovation, leading to the development of complementary technologies and services that further enhance the value proposition of autonomous ride-sharing.
Environmental Implications
Tesla’s commitment to sustainability is exemplified by its Robotaxi service, which promises significant environmental benefits. By replacing internal combustion engine vehicles with electric Robotaxis, Tesla aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decrease the overall carbon footprint of urban transportation.
Autonomous electric vehicles are more energy-efficient than their traditional counterparts, optimizing routes and driving patterns to minimize energy consumption. This efficiency, combined with Tesla’s renewable energy initiatives, positions the Robotaxi service as a critical component of Tesla’s mission to accelerate the transition to sustainable energy.
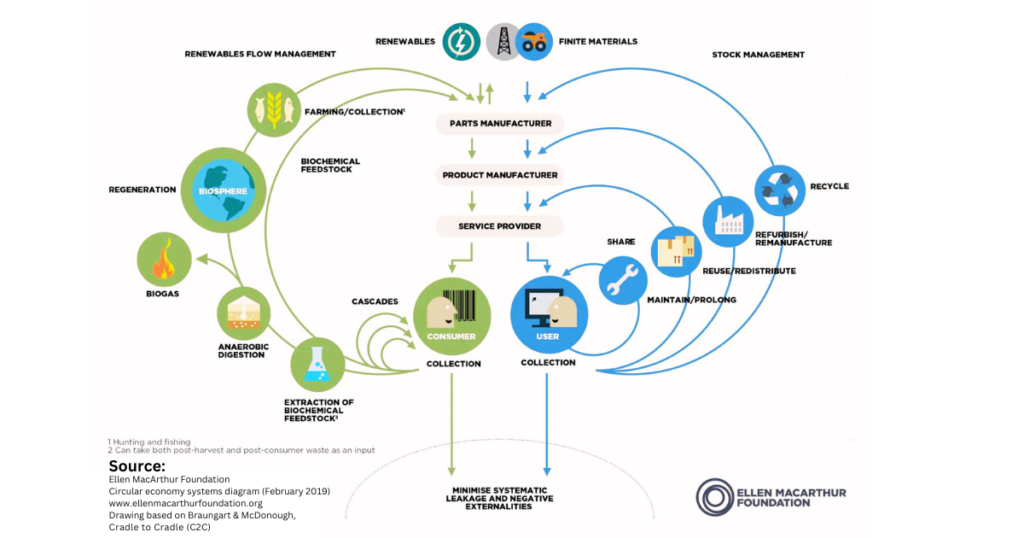
The environmental impact extends beyond immediate emissions reductions. The adoption of Robotaxis could lead to a decrease in vehicle production and resource consumption, as fewer cars are needed to meet the same transportation needs. This shift supports a circular economy model, reducing waste and promoting sustainable practices across the automotive industry.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the promising potential of Tesla’s Robotaxi initiative, several challenges must be addressed before widespread adoption can occur. Regulatory hurdles remain a significant barrier, as governments grapple with the implications of autonomous vehicles on existing transportation frameworks and public safety.
Safety concerns are paramount, with Tesla and other stakeholders working diligently to ensure that autonomous systems meet rigorous standards and can effectively respond to complex driving scenarios. Continued advancements in sensor technology, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data processing are essential to overcoming these challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of autonomous vehicles, including Tesla’s Robotaxi, appears bright. As technology continues to evolve, the prospect of fully autonomous ride-sharing becomes increasingly feasible. With ongoing research and development, Tesla is well-positioned to play a leading role in shaping the future of transportation, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable urban mobility solutions.
Conclusion
Tesla’s Robotaxi initiative represents a paradigm shift in how we perceive transportation, blending cutting-edge technology with sustainable practices to redefine urban mobility. For tech enthusiasts, investors, and industry experts, understanding the potential of this revolutionary service is crucial to navigating the evolving landscape of autonomous vehicles.
By offering a glimpse into the future of transportation, Tesla’s Robotaxi promises to create new opportunities and reshape cities for the better. While challenges remain, the pursuit of a safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly transportation system is within reach.
For those eager to explore the world of autonomous ride-sharing, Tesla’s Robotaxi offers a compelling vision of what lies ahead. Whether you’re a tech aficionado, an investor seeking new opportunities, or an urban commuter looking for more sustainable options, the Robotaxi revolution is poised to make a significant impact on the way we move and live.
In the meantime, keep your eyes peeled for developments in Tesla’s Robotaxi initiative and consider how this innovation could transform your perspective on transportation and urban living.