Brain transplant is a medical procedure that involves replacing a person’s brain with another brain. It is a highly complex and controversial procedure that has been the subject of much debate in the medical community.
In this article, we will explore the history of brain transplants, the science behind it, and the ethical considerations that surround it. We will also discuss the potential benefits and risks of brain transplants, as well as the current state of research in this field.
Brain transplantation is a highly controversial and theoretical procedure involving the transplant of one organism’s brain into the body of another. This differs from head transplants, where the entire head is transplanted into a new body rather than just the brain.
In theory, individuals facing total organ failure could receive a new and functional body through this procedure, maintaining their personality, memory, and consciousness. However, several challenges exist, including the inability of nerve tissue to heal properly, leading to scarring that hinders signal transmission.
What is a brain transplant?
A brain transplant, also known as a whole-brain transplant, is a hypothetical surgical procedure in which a human brain is removed from its original body and placed in a new, healthy body. It is important to distinguish this from a head transplant, which involves transferring the entire head, including the brain and face, into a new body.
It’s a concept that once belonged only to science fiction and has ignited the curiosity and debate of scientists and philosophers alike. It is an idea that is both fascinating and unsettling, promising the possibility of defying death and redefining our understanding of consciousness.
Imagine a scenario where a damaged or diseased brain is carefully removed from its original host and placed inside a new, healthy body. This is the essence of a brain transplant, also known as a whole-brain transplant. It is a hypothetical surgical feat, similar to a heart or kidney transplant, but on an entirely different plane of complexity, penetrating the very core of our being.
Brain vs. Head: A Matter of Distinction
It’s crucial to differentiate brain transplants from head transplants. While both involve placing a human head onto another body, the key distinction lies in what gets transferred. A head transplant involves the entire head, including the brain, skull, face, and all its underlying structures. This intricate procedure remains largely theoretical and faces insurmountable challenges in terms of nerve reconnection and facial reconstruction.
In contrast, a brain transplant focuses solely on the brain itself, leaving behind the original body’s head and face. The extracted brain is then meticulously connected to the new body’s vascular and nervous systems, aiming for seamless integration. While equally complex, this approach avoids the additional challenges associated with transplanting facial features and preserving facial identity.
Brain transplants, while currently in the realm of scientific speculation, offer a tantalizing glimpse into a future where biological boundaries might be redefined. However, the journey towards this future is paved with immense challenges, demanding a cautious and responsible approach that prioritizes ethical considerations and scientific rigor. Only time will tell if this bold venture will become a medical marvel or remain a figment of our scientific imagination.
Is it possible?
Brain transplantation is a highly speculative and controversial topic that is unlikely to become a reality anytime soon due to the many technical and ethical challenges that must be overcome.
Some of the technical challenges include keeping the brain alive during the transplant process, ensuring that the transplanted brain is properly attached to the recipient’s body, and preventing the recipient’s immune system from rejecting the transplanted brain. Ethical concerns include issues of identity, autonomy, and the definition of death.
Although there have been some successful brain transplant experiments in animals, the procedure is far from safe or practical for humans. The living brain is soft and squishy, and it’s easily damaged trying to get it out of one skull and into another. Attempting to transplant a severed brain would require reconnecting many delicate cranial nerves, which would be challenging.
In summary, brain transplantation is a highly speculative and controversial topic that is unlikely to become a reality anytime soon due to the many technical and ethical challenges that must be overcome.
Currently, brain transplants are not possible with our existing technology. The brain is incredibly complex and delicate, and interrupting its blood supply for even a short period of time can cause irreparable damage.
First-Ever Brain Transplant
first ever brain transplant,” it’s important to clarify that no successful brain transplants have been performed on humans to date. It remains a purely hypothetical procedure due to the immense technical and ethical challenges involved.
The history of attempts and research related to brain transplants:
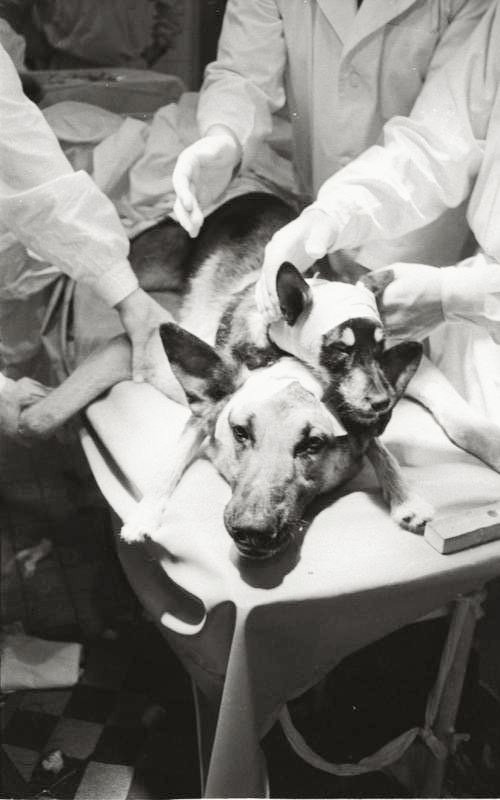
Alexis Carrel and the Two-Headed Dog (1908): French surgeon Alexis Carrel, a Nobel laureate for his work in vascular surgery, embarked on a controversial experiment in 1908. He attempted to transplant the head of one dog onto the body of another. While the surgery appeared successful initially, with the grafted head showing some reflexes, the animal only survived for a few hours. The main challenges Carrel faced included severed nerve connections, inadequate blood supply to the transplanted brain, and rejection by the recipient’s body.
Robert White and the “Reanimated” Monkey Brain (1970s): However, in 1970, neurosurgeon Robert J. White performed a head transplant experiment on two monkeys. He successfully attached the head of one monkey to the body of another. While electroencephalography (EEG) readings initially indicated some brain activity, suggesting function, the procedure wasn’t a complete success. While early reports proclaimed the brain as an immunologically privileged organ due to the lack of immediate rejection, this proved inaccurate. After nine days, the recipient monkey unfortunately succumbed to immune system reactions, highlighting the significant challenges associated with head transplants.
The first successful human brain transplant has not been performed yet. However, in 1970, neurosurgeon First-Ever Brain Transplant conducted an experiment in which he grafted the head of one monkey onto the headless body of another. EEG readings indicated normal brain functioning initially, suggesting the brain’s immunological privilege. However, immunorejection led to the monkey’s death after nine days.
How does this procedure work?
Brain transplant procedures are still largely theoretical and have not yet been performed on humans. However, some researchers propose a method involving the transplant of one organism’s brain into another’s body.
In this procedure, the surgeon first makes an incision at the back of the patient’s head to expose the brain. They then cut through all the connective tissue and vessels linking it to its host body. The spinal cords are severed, and the recipient’s brain and head are transplanted into the new body.
The recipient’s body serves as a transfusion source, and the spine is fused with metal plates while blood supply loop catheters are individually removed as the blood vessels are sutured together.
It’s important to note that brain transplantation is still a highly experimental procedure, and much remains unknown about its safety and efficacy. Therefore, it’s unclear whether the potential benefits outweigh the associated risks and ethical concerns.
In summary, while the process of brain transplantation is largely theoretical, some researchers propose the possibility of transplanting one organism’s brain into another’s body. The procedure involves exposing the brain through an incision in the patient’s head, cutting connective tissue and vessels, and transplanting the brain and head into the new body.
However, brain transplantation remains a highly experimental and controversial procedure, raising numerous ethical questions.
The Challenges for Brain Translation
Brain transplantation is a highly complex and controversial topic that remains largely in the realm of science fiction. While there have been some successful brain transplant experiments in animals, the procedure is currently far from safe or practical for humans.
- Overcoming numerous technical and ethical challenges is necessary before brain implants become a reality, and significant progress in this field may take years if not decades.
- Technical challenges include keeping the brain alive during the transplant process, ensuring proper attachment of the transplanted brain to the recipient’s body, and preventing the recipient’s immune system from rejecting the transplanted organ. Ethical concerns encompass issues of identity, autonomy, and the definition of death.
In summary, brain transplantation is a highly speculative and controversial topic that is unlikely to become a reality anytime soon due to the many technical and ethical challenges that need to be overcome.
The ethical considerations
If brain transplants ever become possible, there would be a host of ethical issues to consider. Who would be eligible for the procedure? How would we ensure informed consent from both the donor and recipient? What would happen to the original body? And what would the psychological and legal implications be of having one brain in two different bodies?
- The ethical implications of brain transplantation are complex and multifaceted. One primary concern is the potential misuse of the method for unethical purposes, such as creating a race of superhumans or prolonging life indefinitely. Additionally, there are worries about the psychological impact on the recipient and the potential loss of identity or personality.
- Another ethical consideration is the issue of consent. Since brain transplantation is a highly experimental procedure not yet performed in humans, uncertainties about its safety and efficacy raise questions about how informed consent can be obtained from patients considering the procedure.
- Concerns also extend to resource allocation, with the possibility that brain transplantation could exacerbate existing healthcare disparities. Given the high cost and complexity of the procedure, it is likely that only a few individuals will be able to afford it, potentially widening the gap in healthcare access.
In summary, brain transplantation, though holding the potential for significant benefits in cases of complete organ failure, remains a highly controversial and theoretical procedure, posing numerous ethical questions. The challenges and limitations associated with this approach must be carefully considered.
What are the potential benefits of a brain transplant?
The potential benefits of brain transplantation are primarily theoretical, as the procedure has not yet been performed on humans.
- Nonetheless, researchers suggest that brain transplants could serve as a means to extend life and enhance the quality of life for individuals with total organ failure. Theoretically, this procedure could provide a new and functional body while retaining the patient’s personality, memory, and consciousness.
- Another potential benefit lies in using brain transplantation to treat certain neurological diseases, such as Parkinson’s disease, by transplanting healthy brain tissue into damaged areas. Although promising results have been observed in animal studies, human trials have not yet been conducted.
It’s crucial to note that brain transplantation remains a highly experimental procedure, and much remains unknown about its safety and efficacy. Consequently, the assessment of whether the potential benefits outweigh the associated risks and ethical concerns remains unclear.
In summary, while brain transplantation holds the potential for significant benefits in treating total organ failure and specific neurological disorders, it is currently a highly experimental and controversial procedure, prompting numerous ethical questions.
The future of brain transplants
Some scientists believe that brain transplantation may become a reality in the future despite the challenges involved. Advances in regenerative medicine, artificial intelligence, and neural interface technology may pave the way for this intricate surgery. However, the concept of brain transplantation raises numerous ethical and practical concerns and remains a subject of debate among experts.
Regenerative medicine focuses on developing therapies to replace or regenerate damaged tissues and organs. Artificial intelligence (AI) involves creating intelligent machines capable of tasks requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation. Neural interface technology encompasses the use of electronic devices to communicate with the nervous system, including brain-computer interfaces (BCIs).
While the idea of brain transplantation may sound like science fiction, some experts believe it could become a reality in the future. However, several challenges must be overcome, including the development of new surgical techniques, ensuring compatibility between donor and recipient, and addressing ethical concerns. Some argue that the idea of brain transplantation is not only impractical but also immoral, raising questions about personal identity, consciousness, and the nature of the self.
In conclusion, although brain transplantation may become a reality in the future, it remains a subject of debate among experts, and numerous challenges must be addressed. Developments in regenerative medicine, artificial intelligence, and neural interface technology may pave the way for this complex surgery, but ethical and practical concerns need careful consideration.