The digital landscape has soared to new heights. More and more businesses are migrating their operations to the cloud, entrusting it with their critical web applications, data, and infrastructure. This paradigm shift, while offering undeniable advantages in scalability and agility, necessitates a robust security apparatus—enter Cloud Web Security.

Cloud Web Security stands as the vigilant protector in this digital realm. It’s a comprehensive strategy encompassing a suite of tools and best practices designed to safeguard web-based applications, data, and the underlying infrastructure residing within the cloud environment.
Just as a physical security system shields a commercial building, Cloud Web Security acts as an invisible force field, deflecting cyberattacks and thwarting malicious attempts to infiltrate the cloud.
Cloud Security VS Cloud Web Security
Cloud web security and cloud security, although closely related, address distinct aspects of safeguarding the cloud environment. Let’s explore their differences:
Cloud Security: Cloud security refers to the umbrella of practices, technologies, and policies designed to safeguard data, applications, and infrastructure residing in the cloud environment.
- Broader Scope: Encompasses the overall protection of data, applications, and infrastructure residing within the cloud.
- Focus: Secures the entire cloud ecosystem, including data at rest, in transit, and during processing.
- Responsibility: Shared between the cloud service provider (CSP) and the organization using the cloud service.
- Measures: Involves data encryption, access control mechanisms, identity and access management (IAM), threat detection & prevention, and adherence to compliance regulations.
Cloud Web Security: Cloud web security builds upon the foundation of cloud security, specifically focusing on protecting web-based elements within the cloud environment.
- Specific Focus: Secures web applications and resources deployed on the cloud platform.
- Protects Against: Web-based threats like injection attacks, cross-site scripting (XSS), denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and malicious code.
- Implementation: Often involves web application firewalls (WAFs), secure coding practices, and vulnerability scanning of cloud-based web applications.
Key Differences:
- Scope: Cloud security addresses the entire cloud environment, while cloud web security specifically focuses on securing web applications within the cloud.
- Responsibility: Cloud security involves a shared responsibility model, whereas cloud web security primarily falls under the organization’s responsibility.
Here’s an analogy:
- Cloud security is like securing your house (the cloud environment) with alarms, security doors, and a monitored security system.
- Cloud web security is like installing additional security measures on your home’s specific entry points (web applications) like reinforced doors and high-security locks.
In essence, cloud security forms the foundation, while cloud web security strengthens specific aspects within the cloud environment. Both are crucial for ensuring a comprehensive security posture in the cloud.
Importance of Cloud Web Security
The adoption of cloud services has revolutionized how businesses operate. However, this shift also introduces security risks. Here’s why cloud web security matters:
- Data Protection: Sensitive information, such as customer data, financial records, and intellectual property, resides in the cloud. Robust security measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Availability and Reliability: Cloud services must be available and reliable. Downtime due to security incidents can disrupt business operations and harm reputation.
- Compliance: Organizations must adhere to industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Proper cloud security ensures compliance.
- Shared Responsibility: While cloud service providers (CSPs) offer secure infrastructure, customers share the responsibility for securing their applications and data.
Benefits of Cloud Web Security
In today’s perilous digital landscape, cyber threats lurk around every corner. Cloud Web Security serves as an unwavering defense against a barrage of malicious activities. Here’s how it bolsters your cloud defenses:
- Shielding Against Digital Onslaught: Cloud Web Security safeguards your web applications from Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks, where malicious actors attempt to overwhelm your systems with a flood of traffic, rendering them inaccessible to legitimate users.
- Eradicating Malicious Code: Cloud Web Security employs advanced techniques to identify and thwart malware injection attempts, where attackers embed malicious code into your applications to steal data or disrupt operations.
- Fortress Around Your Data: Data breaches are a significant concern in the digital age. Cloud Web Security encrypts data at rest and in transit, acting as an impenetrable shield against unauthorized access, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of your sensitive information.
Beyond Security
Cloud Web Security isn’t confined solely to safeguarding your digital assets. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring adherence to an ever-evolving regulatory landscape. By implementing robust cloud security measures, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to meeting industry standards and complying with data privacy regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
One of the significant advantages of cloud-based security solutions lies in their inherent scalability. As your business grows and your cloud footprint expands, Cloud Web Security scales seamlessly to accommodate your evolving needs. Additionally, cloud-based security solutions can offer potential cost benefits. By eliminating the need for upfront investment in hardware and software infrastructure, businesses can leverage the expertise and resources of cloud security providers, often at a predictable and cost-effective rate.
By implementing a comprehensive Cloud Web Security strategy, organizations can venture confidently into the ever-expanding digital frontier. Remember, securing your cloud environment isn’t just about protecting data; it’s about safeguarding your business reputation, fostering trust with your customers, and ensuring the unhindered operation of your mission-critical applications. As the reliance on cloud services continues to surge in 2024 and beyond, mastering Cloud Web Security becomes an essential tenet for guaranteeing a secure and prosperous digital future.
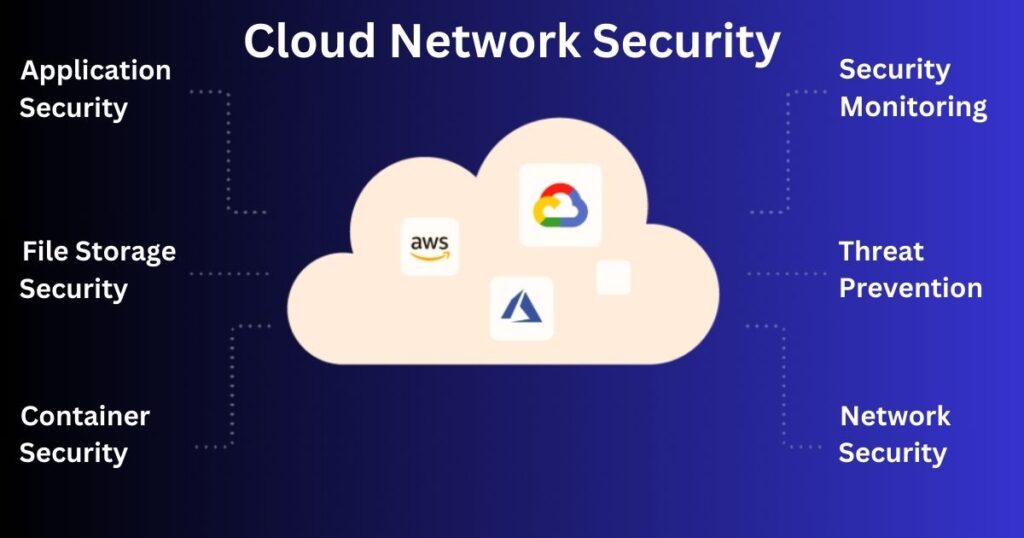
Key Components of Cloud Web Security
In the dynamic landscape of cloud web security, understanding the key components is essential for safeguarding your digital assets. Let’s explore the critical elements that contribute to a robust security posture:
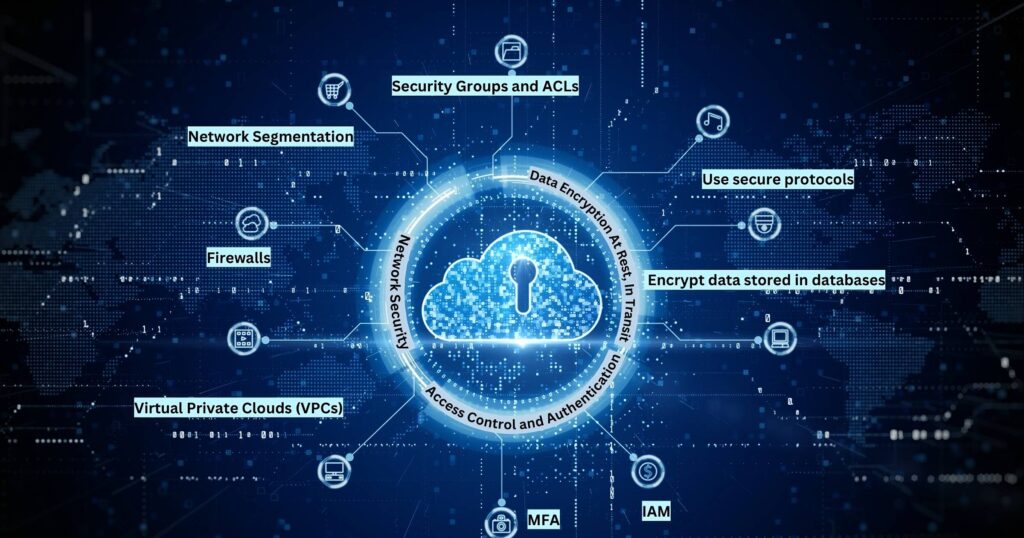
1. Access Control and Authentication
Effective access control ensures that only authorized users can access cloud resources. Consider the following components:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access. Common factors include passwords, SMS codes, biometrics, or hardware tokens. By combining these factors, MFA significantly enhances security.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): IAM is the cornerstone of access control. It allows organizations to manage user permissions and roles systematically. With IAM, you can define who can access specific resources, set fine-grained permissions, and enforce the principle of least privilege.
2. Data Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental practice to protect data from unauthorized access. Consider the following aspects:
- At Rest: Encrypt data stored in databases, object storage, and backups. Whether it’s customer records, financial data, or intellectual property, encryption ensures that even if an unauthorized party gains access to the storage, the data remains indecipherable.
- In Transit: Use secure protocols (such as HTTPS) for data transmission. When data moves between clients, servers, or services, encryption prevents eavesdropping and tampering. It’s crucial for maintaining confidentiality and integrity.
3. Network Security
Securing the cloud network infrastructure is paramount. Consider the following components:
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs): Isolate resources within a private network. VPCs allow you to create logically isolated environments where you can deploy your applications securely. They provide network segmentation, control over IP addressing, and fine-grained security groups.
- Firewalls: Control inbound and outbound traffic. Firewalls act as gatekeepers, filtering traffic based on predefined rules. They prevent unauthorized access, block malicious requests, and ensure compliance with security policies.
- Network Segmentation: Divide networks to limit lateral movement. By segmenting your network, you reduce the attack surface. If an intruder gains access to one segment, they won’t automatically have access to the entire network.
- Security Groups and ACLs: Define rules for traffic flow. Security groups and access control lists (ACLs) allow you to specify which resources can communicate with each other. They act as virtual firewalls at the instance level, controlling traffic at the network interface level.
Now, let’s delve into the critical aspects of Cloud Web Security, focusing on common threats, best practices, and incident response:
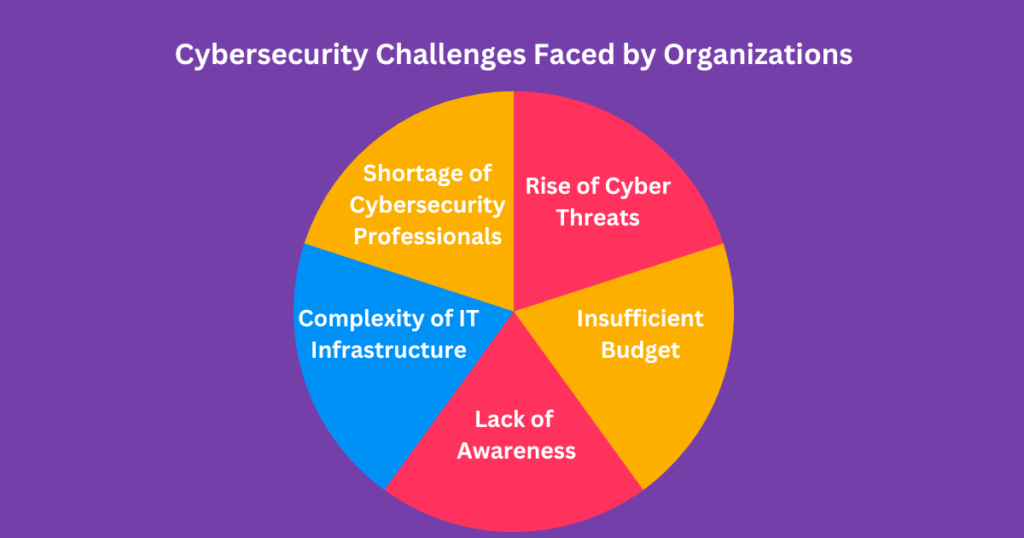
Common Threats and Risks
While the cloud offers undeniable advantages, it also introduces a new battleground for cyber threats. Cloud Web Security becomes paramount in safeguarding your valuable data and applications from a multitude of adversaries.

Here, we delve into some of the most common threats and risks organizations face in the cloud environment:
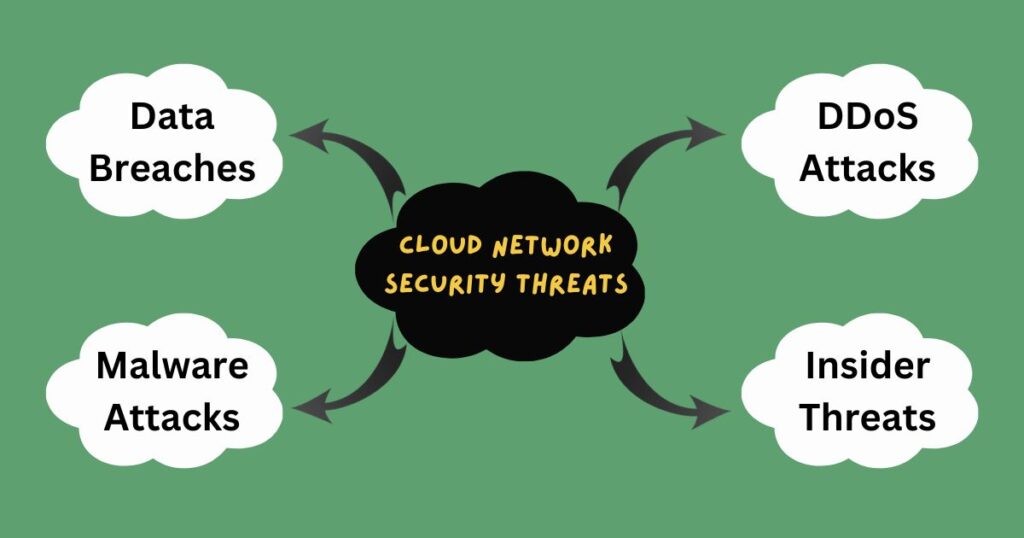
Data Breaches and Unauthorized Access
Data breaches are a constant cause for concern, occurring when sensitive information stored in the cloud is accessed, stolen, or exposed without proper authorization. These breaches can stem from various factors:
- Misconfigured Permissions: Inadequate security protocols or granting excessive access rights can lead to unintended data exposure. Example: A public cloud storage bucket misconfigured to allow public read access, potentially exposing sensitive customer information like financial records or personally identifiable data (PII). A misconfigured Amazon S3 bucket allows public access to confidential customer records.
2. Credential Theft: Malicious actors actively employ various techniques to steal login credentials (usernames and passwords). Example: A phishing campaign successfully tricks an employee into revealing their cloud login credentials, enabling unauthorized access to sensitive data.
3. Insider Threats: Internal actors, including employees, contractors, or partners with malicious intent, can exploit their access to compromise data. Example: A disgruntled employee with access to a customer database downloads and leaks confidential financial information to a competitor.
Malware and Insider Threats
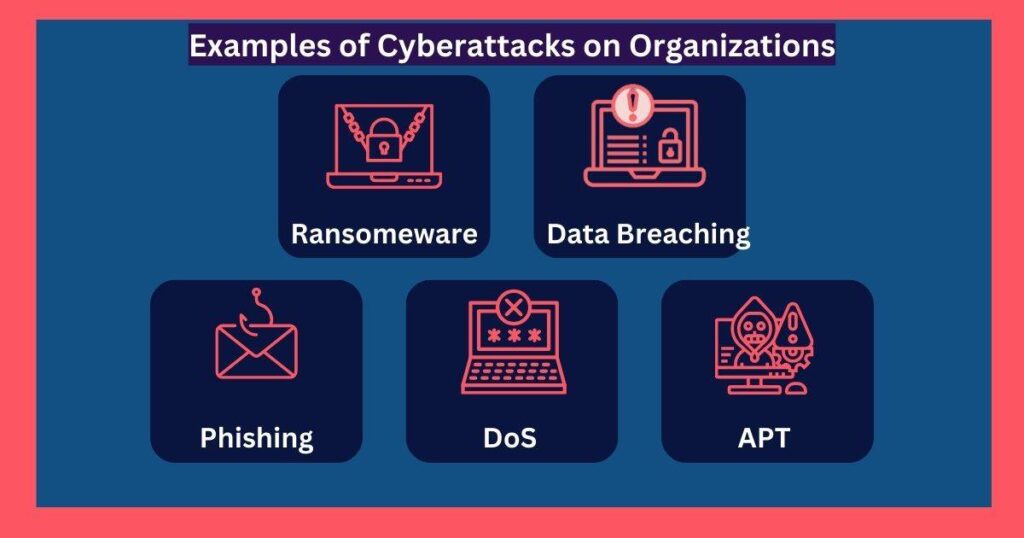
The cloud environment is not immune to malware infiltration. Malicious software (malware) can find its way into cloud systems through various means:
- Cloud Malware Types: Ransomware, trojans, and spyware are some common types of malware that can wreak havoc on cloud-based systems. Example: A cloud server compromised by ransomware encrypts critical data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. A compromised cloud server hosts malware that spreads across the organization’s network.
2. Insider Threats: A Double-Edged Sword: While external threats are significant, insider threats pose a unique challenge due to their inherent level of access and potential for both malicious and unintentional harm: Malicious Insiders: These individuals intentionally exploit their access to steal data, disrupt operations, or plant malware within the cloud environment. Unintentional Insiders: Negligence or lack of proper training can lead to accidental data exposure. Example: A contractor tasked with managing a cloud database accidentally shares sensitive customer information due to a configuration error.
These scenarios highlight the critical need for a robust Cloud Web Security strategy. By implementing a layered defense that includes access controls, data encryption, and user awareness training, organizations can significantly mitigate these risks and safeguard their cloud-based assets. Remember, a vigilant approach is crucial in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats.
Read More: Cloud Network Security | Tech Innovation Pro
Best Practices for Cloud Web Security
Keeping your cloud environment safe is crucial, and we’ve got your back. Securing your cloud environment requires constant vigilance. Here are two essential practices to supercharge your Cloud Web Security:

Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Imagine a security guard meticulously examining every corner of your cloud infrastructure. Regular security audits and assessments function similarly. Imagine you’re giving your entire digital house (the cloud) a thorough inspection now and then. That’s what security audits and assessments do. They involve:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Think of these as automated security guards constantly patrolling your cloud for weaknesses. They identify potential security gaps in your setup, like unlocked doors or hidden crawl spaces.
- Regularly scan cloud resources for vulnerabilities.
- Use automated tools to identify weaknesses in configurations.
- Example: Running vulnerability scans on your cloud servers weekly is like getting regular security reports highlighting areas that need extra attention.
- Penetration Testing: Picture ethical hackers trying their best to break into your cloud, just like a security expert testing your home alarm system. Penetration tests uncover vulnerabilities that real attackers might exploit.
- Simulate attacks to identify security gaps.
- Ethical hackers attempt to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Example: Hiring a penetration testing firm is like inviting security ninjas to try and bypass your defenses, pinpointing areas where intruders might sneak in.
- Compliance Checks: Regularly reviewing your security policies and controls is like checking a compass – it ensures you’re following the right security path and haven’t strayed off course.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., PCI DSS, ISO 27001).
- Regularly review policies and controls.
- Example: Making sure your cloud setup meets GDPR (protecting user privacy in Europe) shows your commitment to keeping user information safe.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
So, we’ve talked about checking your cloud’s defenses regularly, but what about constant vigilance? That’s where continuous monitoring comes in. Imagine having security cameras set up throughout your digital house (the cloud), keeping a watchful eye 24/7. Here’s how it works:
- Real-Time Monitoring: These “security cameras” are advanced tools that constantly monitor your cloud activity for anything out of the ordinary. They’re like having hawk eyes, detecting suspicious activity like unauthorized access attempts or unusual login patterns.
- Implement tools for continuous monitoring.
- Detect anomalies, unauthorized access, and suspicious activities promptly.
- Example: Setting up alerts to notify you whenever someone tries to log in from an unexpected location helps you catch potential security breaches early on.
- Having a Plan B: Even with the best security measures, unexpected situations can arise. That’s why having a comprehensive incident response plan is crucial. Think of it as your personal “fire drill” for the cloud.
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan.
- Define roles, responsibilities, and communication channels.
- Example: Imagine a data breach occurs. By following your pre-defined steps, you can quickly contain the situation, minimize the damage, and get things back on track.
Equipping Yourself for the Journey

Mastering cloud web security is an ongoing pursuit. Here’s your comprehensive toolkit for success:
- Embrace Certifications: Consider pursuing certifications like the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) or the AWS Certified Security – Specialty to validate your expertise and demonstrate your commitment to cloud security best practices. These certifications can also enhance your career prospects in the in-demand field of cloud security.
- Stay Updated: The cloud security landscape is constantly evolving. Subscribe to security blogs from reputable vendors and industry publications. Attend industry events, both physical and virtual, to connect with security professionals and learn about the latest threats and defense strategies. Actively seek out the latest knowledge by participating in online forums and communities dedicated to cloud security.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Set up a lab environment to experiment with security tools and configurations. This hands-on experience will solidify your understanding of cloud security concepts and allow you to test different security approaches in a safe environment. There are many free and paid cloud sandbox environments available that can be used for this purpose.
Conclusion
The digital landscape has soared to new heights, and with this ascension comes the immense responsibility of safeguarding our valuable assets in the cloud. Cloud Web Security isn’t a mere option; it’s the cornerstone of a secure digital future.
Key Takeaways for Unwavering Cloud Security:
- Shared Responsibility: Remember, securing the cloud isn’t a solitary endeavor. Cloud providers offer a robust foundation, but the onus lies with users to configure their environment securely and vigilantly protect their data.
- Knowledge is Power: The ever-evolving threat landscape necessitates staying informed about the latest cyber threats and best practices in Cloud Security.
- Proactive Defense: Implementing a comprehensive Cloud Web Security strategy is paramount. Regular security audits, robust data encryption, and real-time monitoring are the cornerstones of a fortified digital defense.
By prioritizing Cloud Web Security, you not only safeguard your mission-critical applications, data, and infrastructure but also contribute to a more secure online environment for everyone. Investing in web cloud security and cloud application security strengthens the entire digital ecosystem, fostering trust and protecting the integrity of the web.
As we navigate the ever-expanding digital frontier, prioritizing Cloud Web Security becomes an essential tenet for every organization. By understanding the shared responsibility, staying informed about evolving threats, and implementing robust security measures, you can ensure a secure and prosperous digital future.
Remember, online security starts with securing your cloud environment – and with the right approach, you can transform your cloud into a safe and reliable haven for your data and applications.
What are the benefits of Cloud Web Security?
Enhanced Protection: Protects data from breaches using encryption and access controls.
Scalability: Easily adjusts security measures to meet changing needs.
Threat Detection & Prevention: Advanced tools identify and block cyberattacks.
How Does Cloud Web Security Work?
Security measures like firewalls and intrusion prevention stop suspicious activity.
Cloud-Based Web Filtering:
Filters web traffic to block access to malicious websites and content.
Cloud Web Security Scanner:
Analyzes websites for vulnerabilities and security risks.
Cloud Web Security Connector:
Integrates cloud security services with existing IT infrastructure.
What is cloud-based web filtering?
Location: Hosted on a remote server (the cloud) by a security provider.
Function: Analyzes web traffic in real-time.
Action: Blocks access to harmful websites and content:Malicious sites containing malware or phishing attempts.
Inappropriate content based on pre-defined categories (e.g., gambling, adult content).
What are the 4 types of cloud computing?
Public Cloud: Shared resources delivered over the internet (e.g., Amazon Web Services).
Private Cloud: Dedicated cloud infrastructure for a single organization.
Hybrid Cloud: Combines public and private cloud resources.
Multi-Cloud: Utilizes multiple public cloud providers.