3D printing is a manufacturing process that creates a three-dimensional object from a digital model. The process works by building up layers of material, one on top of the other until the desired object is complete.
In more everyday terms, 3D printing uses a special printer to make a physical, solid object based on a 3D digital design. It does this by slowly depositing thin layers of material in precise shapes until an object like a cup, a toy, or a spare part is formed.
3D printing technology allows objects of nearly any shape to be produced, optimized for the exact needs and customization required. Different materials, like plastics, metals, or even living cells, can be used as printing materials.
The key takeaway is that 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that constructs objects layer-by-layer based on digital 3D models. It opens up new creative possibilities and customization for all kinds of applications.
How has 3D printing evolved? A brief history and trajectory
3D printing was first invented in the 1980s, but it has only become mainstream in recent years. This is due to a number of factors, including the development of new technologies, the reduction in the cost of 3D printers, and the growing awareness of the benefits of 3D printing.
Key milestones in the evolution of 3D printing:
- 1983: Charles Hull invented the first Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printer.
- 1986: Carl Deckard invents the selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printer.
- 1992: Scott Crump invents the fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printer.
- 2005: The RepRap project is launched, which aims to create a self-replicating 3D printer.
- 2009: The MakerBot Cupcake 3D printer is released, making 3D printing more accessible.
- 2012: The first 3D-printed car is unveiled.
- 2013: NASA uses 3D printing to create tools for astronauts on the International Space Station.
- 2014: The first 3D-printed house is built.
- 2015: The first 3D-printed prosthetic leg is approved by the FDA for commercial sale.
- 2016: The first 3D-printed heart is successfully transplanted into a mouse.
- 2017: The first 3D-printed bridge is built in the Netherlands.
- 2018: The first 3D-printed rocket engine is test-fired by NASA.
- 2019: The first 3D-printed food restaurant opened in Moscow, Russia.
- 2020: The first 3D-printed houses were built in Mexico and the United States.
- 2021: The first 3D-printed meat is produced by a company called Aleph Farms.
- 2022: The first 3D-printed human skin was created by researchers at the University of California.
- 2023: The first 3D-printed heart valve is implanted into a human patient.
These are just a few examples of the many ways that 3D printing is being used to revolutionize various industries and applications. As the technology continues to develop and become more affordable, we can expect to see even more innovative and groundbreaking uses for 3D printing in the years to come.
In addition to the milestones above, here are some other notable recent developments in 3D printing:
- Multi-material 3D printing: 3D printers that can print with multiple materials are becoming increasingly common. This allows for the creation of more complex and functional objects with a wider range of properties.
- Metal 3D printing: Metal 3D printing is also becoming more widespread. This is opening up new possibilities for manufacturing metal parts for a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, and medical.
- Bioprinting: Bioprinting is a type of 3D printing that is used to create living tissues and organs. This technology has the potential to revolutionize medicine and regenerative medicine.
3D printing is a rapidly developing technology with the potential to transform many industries and aspects of our lives. The milestones and developments listed above are just a glimpse of what is to come.
When did 3D printing become mainstream?
3D printing became mainstream in the early 2010s, with the release of affordable 3D printers such as the MakerBot Cupcake. The launch of the RepRap project also played a role in making 3D printing more accessible to consumers.
Prior to the early 2010s, 3D printers were very expensive and primarily used in industrial and commercial settings. However, the release of the MakerBot Cupcake in 2009 made 3D printing more accessible to consumers, with a price tag of just $1,200. The RepRap project, which was launched in 2005, aimed to create a self-replicating 3D printer, which would further reduce the cost of 3D printing.
In addition to the release of affordable 3D printers, the growing popularity of the maker movement also helped to mainstream 3D printing. The maker movement is a culture of DIY and innovation, and 3D printing was a natural fit for the maker community. Makers were able to use 3D printing to create custom objects, prototypes, and even entire products.
The mainstreaming of 3D printing has had a significant impact on a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, education, and the arts. 3D printing is now used to produce everything from medical implants to custom shoes to architectural models.
Where is 3D printing used today?
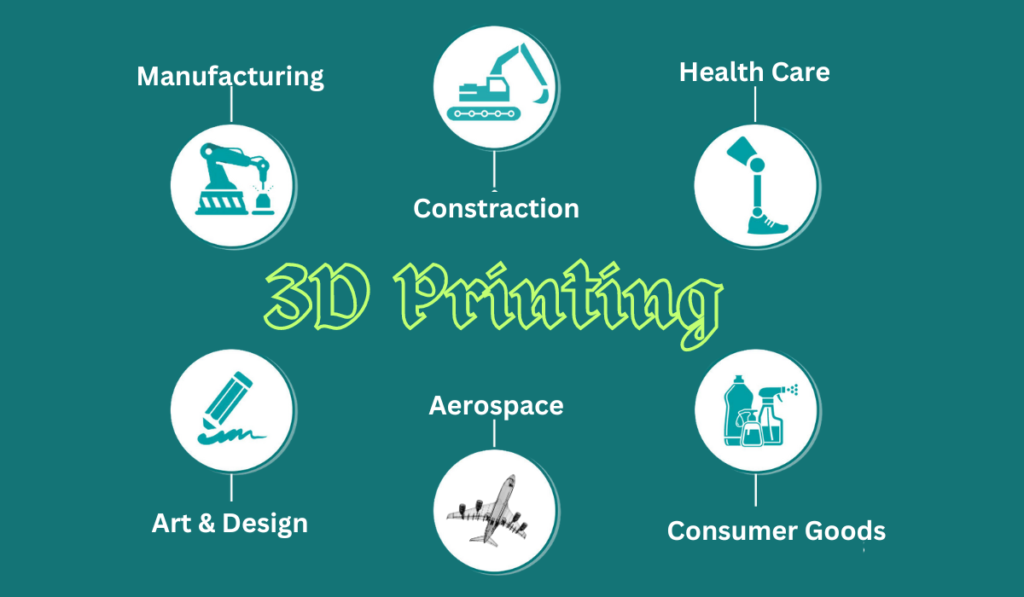
3D printing is used in a wide range of industries and applications, including:
- Manufacturing: 3D printing is used to create prototypes, tooling, and end-use parts.
- Design: 3D printing is used to create concept models, prototypes, and finished products.
- Healthcare: 3D printing is used to create medical devices, prosthetics, and implants.
- Aerospace: 3D printing is used to create lightweight and complex parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
- Automotive: 3D printing is used to create prototypes, tooling, and end-use parts for cars and trucks.
- Consumer goods: 3D printing is used to create custom products such as jewelry, toys, and home decor.
Why does 3D printing matter?
3D printing has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing and design. It offers a number of advantages over traditional manufacturing methods, including:
- Flexibility: 3D printing can be used to create objects with complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional methods.
- Customization: 3D printing can be used to create customized products for individual customers.
- Speed: 3D printing can be used to create prototypes and small batches of products quickly and efficiently.
- Cost: 3D printing can be used to reduce the cost of manufacturing certain products.
- No Assembly: 3D printed objects are constructed as one solid piece with no assembly required. This enables monolithic structures.
- Sustainability: Additive 3D printing has less material waste than subtractive manufacturing methods like machining, casting or forging. It uses only the required material.
- Democratized Manufacturing: 3D printing enables decentralized manufacturing, allowing anyone to become a manufacturer with the right equipment. This disrupts traditional mass production.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: 3D printing on-demand and on-site reduces logistics needs and supply chain costs. Products can be printed where and when they are required.
- Invention Platform: 3D printing fosters innovation by allowing inventors and entrepreneurs to rapidly develop and iterate prototypes to turn ideas into products.
- Healthcare Advances: Customized medical devices, implants, and living tissues are being 3D printed, improving treatment options.
3D printing enables creativity, sustainability, flexibility, and access to manufacturing in unprecedented ways. It empowers decentralized, localized production and is reinventing supply chains. This technology will have far-reaching impacts across industries.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Forget replicators from sci-fi movies. 3D printing is real, but the process is way cooler than waving your hand! It’s all about building things up, layer by layer, like a mini-construction crew working for your imagination. Imagine building a cake, but instead of frosting, you use melted plastic or other materials. Each layer adds definition until your design comes to life!
Here’s a simplified breakdown:
1. Design Your Masterpiece: First, you create a digital model of your object using 3D design software. Think of it as a blueprint for your creation.
2. Slicing Up the Fun: The software then slices your design into thin, digital layers, like pages in a book. Each page represents one layer your printer will build.
3. Printing in Action: Now comes the printing magic! Your chosen printer reads the sliced file and, depending on the technology, does one of these things:
- Melts and extrudes plastic: Similar to a hot glue gun, the printer melts plastic filament and deposits it layer by layer, following the design instructions.
- Cures liquid resin: A laser beam precisely scans and hardens liquid resin layer by layer, forming your object.
- Binds powdered materials: The printer selectively binds together tiny particles of powder with glue or heat, building your design one layer at a time.
4. Layer-by-Layer Wonders: With each layer solidifying, your object takes shape, rising from the print bed like a 3D timelapse! The process can take minutes or hours, depending on the size and complexity of your design.
5. Voila! Your Creation Awaits: Once printing is complete, you might need to remove support structures and do some light finishing. But then, behold! You hold your unique, 3D-printed masterpiece in your hands, ready to use, display, or share!
What You Can Make with 3D Printing
The beauty of 3D printing lies in its limitless potential. No longer confined to traditional manufacturing constraints, your imagination truly becomes the blueprint. Here’s just a glimpse of the diverse possibilities at your fingertips:
Functional Everyday Items:
- Household tools and organizers: Custom hooks, phone stands, cable clips, storage containers, drawer dividers – anything to declutter and personalize your space.
- DIY repairs and replacements: Broken doorknobs, missing furniture parts, malfunctioning gadget pieces—3D printing can often save the day (and a trip to the store).
- Personalized wearables and accessories: Phone cases, jewelry, keychains, even shoes—unleash your inner designer and create unique pieces that reflect your style.
Creative Expression and Art:
- Sculptures and figurines: Bring your artistic vision to life, layer by layer. You can even replicate real-world objects with stunning detail.
- Custom toys and game pieces: Design imaginative toys for your kids or unique game pieces for family game nights.
- Decorative home accents: Vases, lamps, coasters, wall art – the possibilities are endless, and you can customize them to match your décor.
Practical Applications and Prototyping:
- Educational tools: Models of historical figures, anatomical models, puzzles, and interactive learning aids—bring complex concepts to life in a tangible way.
- Medical and dental applications: Prosthetics, custom casts, braces, and even dental implants—3D printing is revolutionizing healthcare.
- Prototyping and product design: Quickly and affordably create functional prototypes to test, iterate, and refine your product ideas before mass production.
Just remember, this is just the tip of the iceberg! The world of 3D printing is constantly evolving, with new materials, techniques, and applications emerging all the time. What will you create next?
What’s next for 3D printing?
Some of the upcoming innovations and trends in 3D printing include:
- New materials: New 3D printing materials are being developed that have different properties, such as strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility.
- Faster printing speeds: 3D printers are becoming faster and more efficient.
- Larger build volumes: 3D printers with larger build volumes are being developed, which will allow for the printing of larger objects.
- Multi-material printing: 3D printers that can print multiple materials at the same time are being developed.
- Bioprinting: Bioprinting is a type of 3D printing that is used to create living tissues and organs.
Conclusion
3D printing is a rapidly evolving technology that promises to revolutionize manufacturing and design. It enables on-demand, customized production without assembly using digital files and additive printing. As 3D printing advances, it will transform supply chains through localized manufacturing. It also unlocks creative possibilities and sustainability benefits with reduced waste.
The technology is already used across industries today, and it will only grow. 3D printing allows inventions once impossible to become reality. It empowers businesses of any size to become producers. This technology will undoubtedly transform production and business models across sectors for years to come. Its full potential is still being unlocked, but 3D printing is undoubtedly one of the most disruptive and empowering technologies of our time.
How does 3D printing work?
What are the different types of 3D printers?
1. FDM (fused deposition modeling): FDM printers are the most common type of 3D printer. They work by depositing a thermoplastic filament onto the build platform layer by layer.
2. SLA (stereolithography): SLA printers use a laser to cure a liquid resin into a solid object.
3. SLS (selective laser sintering): SLS printers use a laser to sinter a powder material into a solid object.
