
Renewable energy sources are at the forefront of a global shift towards sustainable and environmentally friendly alternatives. Defined as natural resources replenishable on a human timescale, these sources encompass solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy.
The ongoing innovation and adoption of these resources have not only revolutionised the energy landscape but also significantly impacted environmental, economic, and energy security dimensions. This comprehensive overview will delve into the definition and types of renewable energy sources, examining their pivotal role in shaping our world.
From the fundamental technologies driving solar power systems to the historical evolution of renewable energy adoption, we will explore the major projects globally and underscore the critical importance of embracing renewable energy. Additionally, we will delve into the ongoing innovations in renewable technology, such as new solar cell materials, floating offshore wind farms, concentrated solar power (CSP), tidal energy, and wave energy.
What are the renewable energy sources?
In the face of growing environmental concerns and the imperative to transition towards sustainable energy solutions, the exploration of renewable energy sources has become paramount. Renewable energy sources are natural resources that can be replenished on a human timescale. They include solar energy, wind energy, hydropower, geothermal energy, and biomass energy.

- Solar energy: Solar energy is the energy from the sun that is converted into electricity or heat using photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar thermal collectors.
- Wind energy: Wind energy is the energy from the wind that is converted into electricity using wind turbines.
- Hydropower: Hydropower is the energy from moving water that is converted into electricity using turbines.
- Geothermal energy: Geothermal energy is the heat from the Earth’s core that is used to generate electricity or heat homes and buildings.
- Biomass energy: Biomass energy is the energy from organic matter, such as plants and wood, that is converted into electricity or heat using combustion or other processes.
How do solar power systems work?
Solar power systems work by using photovoltaic (PV) cells to convert sunlight into electricity. PV cells are made of semiconductor materials like silicon that can release electrons when hit by photons of sunlight. This generates a flow of electrons, creating a direct electric current. The solar panels contain these PV cells to absorb and convert the maximum amount of sunlight. The direct current then goes into an inverter, which transforms it into alternating current that can be used to power home devices and appliances. Excess electricity can be stored in batteries. So in summary, the photovoltaic cells in the solar panels capture and convert the sun’s energy into direct current electricity.
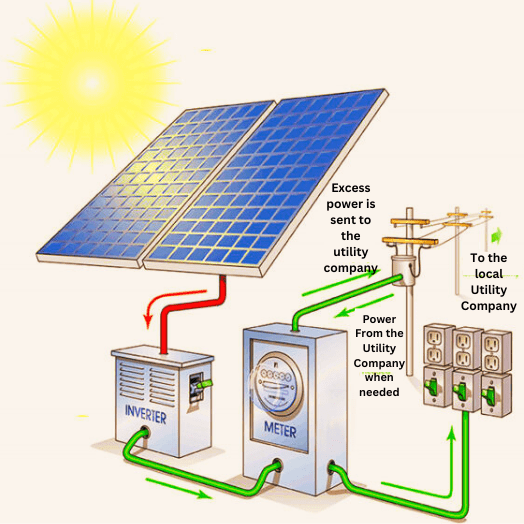
Then the inverter changes this electricity into usable alternating current for the home. Batteries store surplus electricity. This allows the free power of sunlight to be utilised as a clean, renewable energy source.
When Did renewable energy adoption begin?
The adoption of renewable energy began in the early 1900s with the development of hydroelectric power. However, it was not until the late 1970s and early 1980s, during the oil crisis, that renewable energy sources began to receive serious attention.
Since then, there has been a steady increase in the adoption of renewable energy. In 2021, renewable energy accounted for 29% of global electricity generation.
Read: What is a Smart City? Unveiling the Future
Where are the major renewable energy projects? Examples around the world.
There are major renewable energy projects underway all over the world. Here are a few examples:
- China: China is the world leader in renewable energy, with over 1,000 gigawatts of installed renewable capacity. The country is home to some of the world’s largest solar and wind farms.
- United States: The United States is the second-largest renewable energy market in the world, with over 300 gigawatts of installed renewable capacity. The country is home to some of the world’s largest solar and wind farms, as well as a growing geothermal and hydropower industry.
- Europe: Europe is a major market for renewable energy, with over 400 gigawatts of installed renewable capacity. The region is home to some of the world’s largest offshore wind farms, as well as a growing solar and biomass energy industry.
- India: India is the fourth-largest renewable energy market in the world, with over 150 gigawatts of installed renewable capacity. The country is home to some of the world’s largest solar and wind farms, as well as a growing hydropower industry.
- Brazil: Brazil is the fifth-largest renewable energy market in the world, with over 150 gigawatts of installed renewable capacity. The country is home to some of the world’s largest hydropower plants, as well as a growing solar and wind energy industry.
Why is adopting renewable energy important?
There are many benefits to adopting renewable energy, including:
- Environmental benefits: Renewable energy sources are clean and do not produce greenhouse gas emissions. This helps to reduce air pollution and combat climate change.
- Economic benefits: Renewable energy can create jobs and boost the economy.
- Energy security: Renewable energy sources can help to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels.
What are the next innovations in renewable tech?
There are a number of innovations in renewable technology that are currently under development. These include:
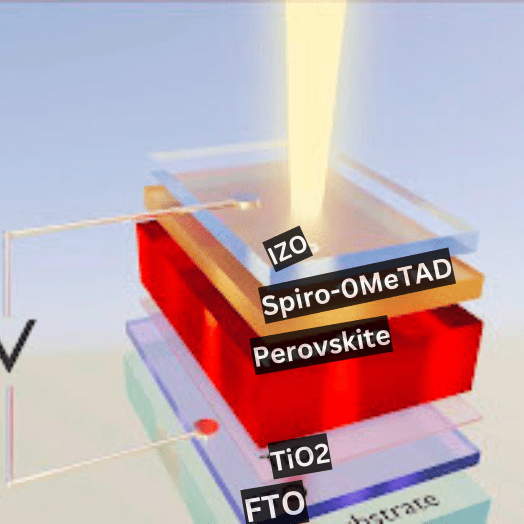
New solar cell materials: Researchers are developing new solar cell materials that are more efficient and less expensive than traditional silicon cells. One example is Perovskite Solar Cells, which have the potential to achieve efficiencies of over 30%.
Floating offshore wind farms: Floating offshore wind farms can be built in deeper waters than traditional fixed-bottom wind farms, which opens up new areas for wind energy development. The first floating offshore wind farm, Hywind Scotland, was installed in 2017.


Concentrated solar power (CSP): CSP plants use mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a receiver, which heats a fluid to generate steam. The steam then drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP plants can achieve higher efficiencies than traditional solar PV systems, but they are also more expensive.
Tidal energy: Tidal energy is the energy from the movement of the tides. Tidal turbines can be installed in coastal areas to generate electricity. Tidal energy is a predictable source of energy, but it is only available in certain locations.
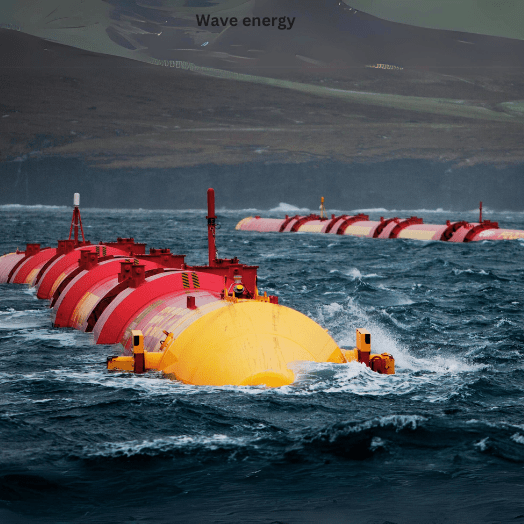
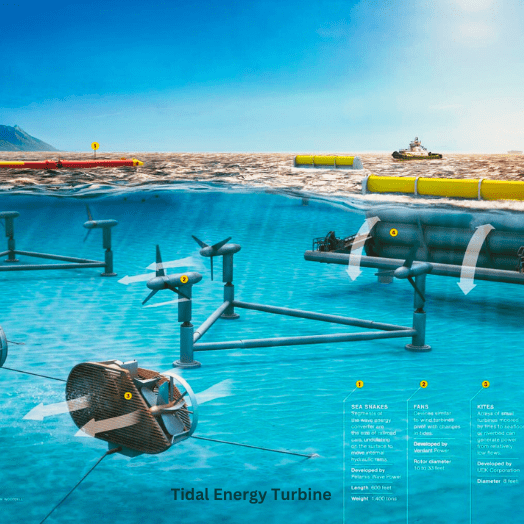

Wave energy: Wave energy is the energy from ocean waves. Wave energy converters can be installed offshore to generate electricity. Wave energy is a highly variable source of energy, but it has the potential to generate a significant amount of electricity.
These are just a few examples of the many innovations in renewable technology that are currently under development. As these technologies continue to mature and become more cost-effective, they are poised to play a major role in the global energy transition.
Conclusion
Renewable energy technology is transforming the world. Renewable energy sources are now clean, affordable, and reliable. They are being used to generate electricity, power homes and businesses, and even transportation.
The next generation of renewable energy technologies is even more promising. These technologies are more efficient, less expensive, and can be deployed in a wider range of locations.
As renewable energy technology continues to develop and improve, it is poised to play a major role in the global transition to a clean energy future.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.