Navigating through the landscape of cloud network technology reveals a realm of innovative strategies and robust solutions designed to propel businesses forward.
From the intricate design of cloud network architecture to the tailored security measures safeguarding data, companies are exploring diverse cloud networks to enhance their operational efficiency and scalability.
Understanding the nuances of virtual networks, from SDN (Software-Defined Networking) to hybrid cloud networking, is crucial for optimizing performance and managing costs effectively.
Integrating AI and machine learning, alongside strategies for efficient cost management during migration, further enriches this landscape. In this article, we will discover powerful techniques and practical solutions in the realm of cloud networking.
Exploring the Types of Cloud Networks for Business
Embarking on the journey toward adopting cloud network technology requires a nuanced understanding of its diverse ecosystems, specifically public, private, and hybrid cloud basics.
This understanding forms the bedrock upon which businesses can align their operational needs and objectives with the most suitable cloud solution.
Navigating through the cloud’s intricate landscape, from cloud network architecture to cloud security, demands a strategy that not only addresses immediate needs but is also scalable for future growth.
As we delve deeper into the types of cloud networks, remember, that the choice between a virtual network, a cloud WAN, or a hybrid cloud networking solution isn’t merely about data storage locations; it’s about crafting a network that resonates with the pace and scale of your business aspirations.
This section lays a comprehensive foundation, guiding you through these critical choices to ensure your business not only thrives but excels in leveraging cloud capabilities.
Understanding Public, Private, and Hybrid Cloud Basics
Grasping the basic concepts of public, private, and hybrid cloud networks forms the cornerstone of any digital transformation strategy. For a long time, my journey in deciphering the complexities of cloud network technology reinforced the importance of aligning business infrastructure with cloud environments that best fulfill organizational goals and requirements.
Public clouds offer a vast, on-demand infrastructure managed by third-party providers, eliminating the need for businesses to invest in and maintain their own physical servers. In contrast, private clouds provide a dedicated environment controlled entirely by the organization, offering a greater level of security and customization.
Meanwhile, hybrid cloud networking bridges the gap, combining the scalability and cost-efficiency of public clouds with the control and security of private clouds, creating a flexible and dynamic networking ecosystem tailored to a business’s unique needs.
Matching Your Business Needs to the Right Cloud Solution
Identifying the right cloud solution for your business is akin to piecing together a puzzle where each piece represents a different aspect of your operational needs. Whether it’s the agility and expansiveness of cloud WAN, the meticulous control and privacy offered by a private cloud, or the innovative approach of SDN (Software-Defined Networking), the goal is to find a solution that not only fits today’s objectives but also adapts to future demands.
Through my experience, leveraging a hybrid cloud networking strategy often emerges as a powerful solution, especially for businesses navigating the complexities of integrating legacy systems with modern cloud applications. This approach allows for a seamless blend of network virtualization technologies, including cloud VPNs for secure remote access and multi-cloud networking strategies to optimize performance and costs.
Ultimately, the choice is driven by a thorough assessment of cloud security requirements, data accessibility needs, and the overarching ambition to harness the cloud’s potential for innovation and growth.
Ensuring Security in Your Cloud Network Infrastructure
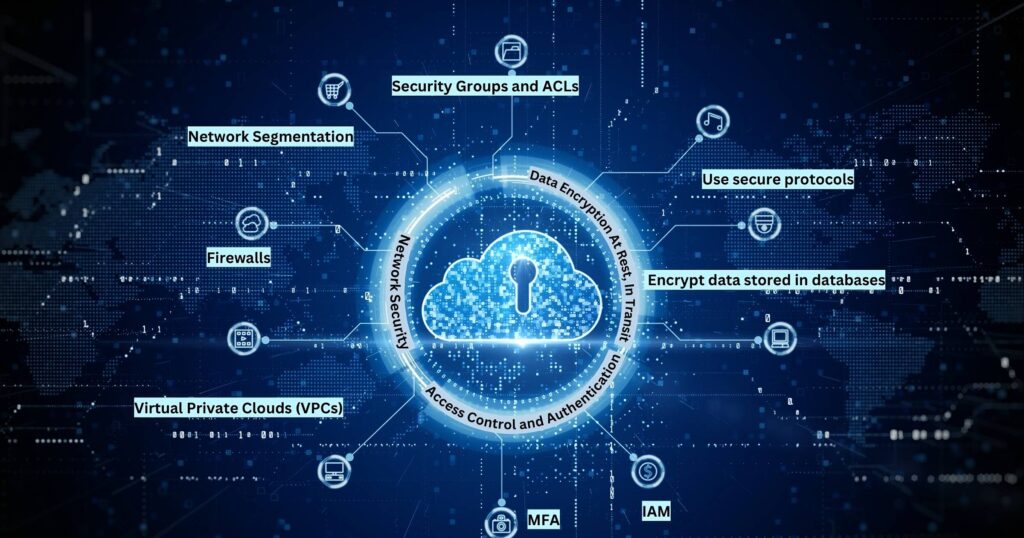
Securing cloud network infrastructure isn’t just about erecting barriers; it’s about creating a robust framework that ensures the integrity and confidentiality of data as it moves through the virtual expanse of the cloud.
As I’ve navigated through the complexities of cloud networking, it’s become increasingly clear that the foundation of a secure cloud environment hinges on not only where data is stored but also on how it is accessed and transmitted.
By focusing on best practices for secure data storage and transmission, including the adoption of multi-factor authentication and comprehensive encryption strategies, businesses can significantly mitigate risks, turning their cloud network into a fortress that safeguards their most valuable assets while fostering an environment of trust and reliability.
Best Practices for Secure Data Storage and Transmission
In my journey through the landscape of cloud network technology, I’ve learned that the art of securing data in transition presents a unique set of challenges. Emphasizing encryption becomes paramount, as it transforms sensitive information into unreadable text for anyone without the decryption key, ensuring that data remains protected as it traverses across the cloud.
Another critical lesson was the importance of adopting a holistic viewpoint toward access control mechanisms within the cloud network. By meticulously crafting who has permission to both view and manage data, I’ve seen first-hand how businesses significantly lower the risk of unauthorized access, reinforcing the security framework surrounding their cloud-based assets.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication and Encryption
In my professional journey, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) became a pivotal strategy in enhancing the security of cloud network infrastructures. By integrating this layer, I made it considerably harder for unauthorized users to gain access, as it requires them to provide two or more verification factors to authenticate their identity, far beyond just a password.
Alongside MFA, diving deep into encryption strategies taught me the non-negotiable importance of protecting data at rest and in transit. By converting sensitive information into a code accessible only through a decryption key, I fortified the cloud environment against breaches and leaks, fostering a secure ecosystem for sensitive data across the virtual landscape.
Optimizing Performance in Cloud Network Environments

In my exploration of cloud network technology, a pivotal focus has been on enhancing performance across the board.
A common hurdle I’ve encountered involves the latency inherent in distributed networks—how it can impair user experience and slow down operations.
My strategy to counteract this involves two critical techniques: reducing latency through strategic interventions and leveraging the power of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to accelerate access to data.
Each method has proven to be instrumental in smoothing out performance peaks and troughs, ensuring that the network’s speed matches the pace of business demands.
Techniques for Reducing Latency in Distributed Networks
In my journey through the nuanced realm of cloud network technology, an innovative real-world approach has been adopting SDN (Software-Defined Networking) to dynamically manage and optimize the network. SDN’s ability to programmatically configure network resources and prioritize data packets significantly cuts down latency, proving to be a game-changer in maintaining high-speed operations across distributed networks.
Another strategy that has markedly influenced the performance metrics within cloud environments is the strategic placement of cloud VPN endpoints. By situating these access points closer to the user’s location, the communication path is shortened, inherently reducing travel time for data. This adjustment can lead to a palpable decrease in latency and an enhanced overall user experience, showcasing the tangible benefits of a meticulously planned cloud network architecture.
Leveraging Content Delivery Networks for Improved Speeds
In my quest to uplift cloud network performance, embracing Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) emerged as a critical momentum builder. These networks adeptly cache content at numerous points across the globe, ensuring users receive data from the nearest server, significantly boosting speed and reducing server load.
My implementation of CDNs has vividly transformed the accessibility and reliability of digital resources, redefining user experiences by minimizing delays in content delivery. This approach harnesses geographical diversity to optimize network efficiency, a testament to the innovative realm of network virtualization and its capacity to elevate the performance standards of cloud networking environments.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Cloud Networking
The transformative impact of AI and machine learning in cloud network technology cannot be overstated, especially as businesses seek more sophisticated ways to optimize and secure their cloud environments.

By integrating AI tools for automating network management tasks, organizations can not only streamline operations but also significantly reduce the risk of human error.
Similarly, machine learning algorithms play a vital role in enhancing predictive analytics, providing insights that allow for proactive adjustments to network configurations based on real-time data.
This fusion of AI and machine learning is revolutionizing the way we approach cloud network architecture, paving the way for more intelligent, autonomous systems that adapt and evolve in response to an organization’s changing needs.
Automating Network Management Tasks With AI Tools
In my career, I’ve witnessed the transformational power of integrating AI tools into routine network management tasks. This innovation brings a new level of efficiency, enabling networks to self-monitor, self-configure, and even self-heal, dramatically reducing the time IT teams spend on day-to-day maintenance.
Embracing AI-driven automation has also allowed me to preemptively identify network vulnerabilities and performance issues before they escalate.
This preemptive approach, powered by sophisticated AI algorithms, shifts the paradigm from reactive to proactive network management, ensuring seamless operations and a superior user experience.
Enhancing Predictive Analytics With Machine Learning Algorithms
In my line of work, the application of machine learning algorithms has been a critical factor in amplifying predictive analytics capabilities within cloud network environments. These algorithms analyze patterns and trends from vast datasets, allowing us to forecast future network demands and challenges with remarkable accuracy.
This foresight enables me to tailor network resources and configurations preemptively, ensuring the infrastructure can handle upcoming loads or threats without a hitch. The integration of machine learning into cloud networking has not only streamlined operational efficiency but also elevated the predictability and reliability of network performance.
Managing Costs While Migrating to a Cloud Network
Migrating to a cloud network presents an exciting frontier for enhancing business operations, yet managing the associated costs demands a strategic approach.
In my experience, the transition to cloud-based infrastructure, while promising significant benefits, also introduces complexities in cost management and optimization.
Identifying cost-effective strategies for this migration is crucial to ensuring that businesses not only benefit from the technological advantages but also maintain financial viability and efficiency throughout the process.
The pursuit of finding the balance between leveraging advanced cloud network features and managing expenditures has propelled me to explore and implement practical solutions designed to mitigate costs without compromising on the quality or scalability of the cloud infrastructure.
Identifying Cost-Effective Strategies for Migration
In my professional journey towards optimizing cloud network migrations, I’ve discovered that a thorough assessment of existing infrastructure is imperative. Such evaluations allow me to pinpoint areas where transitioning to the cloud would not only enhance efficiency but also lead to significant cost savings, avoiding unnecessary expenditures on migrating resources that are already operating optimally on-premise.
Another pivotal strategy I’ve employed involves negotiating scalable contracts with cloud service providers. This flexibility ensures that the business only pays for the resources it actually uses, preventing overinvestment in capacity that might not be needed immediately but can be scaled up as the organization grows and its cloud networking demands evolve.
Conclusion
Navigating cloud network technology with strategic acumen and selecting the appropriate solutions is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage the cloud’s potential effectively.
By understanding the distinct characteristics and benefits of public, private, and hybrid clouds, businesses can align their operational needs and future goals with the right cloud environment, ensuring scalability, security, and performance.
Employing hybrid cloud strategies and embracing innovations such as SDN, cloud VPNs, and multi-cloud networking can optimize both cost and efficiency, providing a tailored approach to meeting specific business requirements.
Additionally, prioritizing security through encryption, multi-factor authentication, and best practices in data management protects valuable assets in the cloud. Optimizing performance by reducing latency and leveraging CDNs enhances user experience and operational speed.
Furthermore, integrating AI and machine learning into cloud networking automates tasks, enhances predictive analytics, and fosters a more responsive, autonomous network infrastructure.
Lastly, managing migration costs effectively ensures that businesses can enjoy the technological and operational benefits of cloud networking without compromising their financial health.
Overall, a strategic approach to navigating cloud network technology lays a foundation for innovation, growth, and long-term success in the digital landscape.