“Cybersecurity in the Digital Age” has become an indispensable shield for both individuals and organizations alike. In an interconnected world, this term embodies the critical practice of safeguarding not only the computer systems, networks, and sensitive data of organizations but also the personal information of individuals. As cyber threats continue to evolve in sophistication and frequency, the need for robust cybersecurity has never been more paramount.
Within this ever-expanding realm, both organizations and individuals must bolster their defenses with effective cybersecurity measures. These measures are the bastions against an extensive array of threats, ranging from the humble computer virus to the ominous specter of ransomware. The professionals entrusted with this crucial mission employ an arsenal of technologies and best practices, harnessing advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation to shield against the ceaseless march of digital adversaries.
To strengthen cyber defenses, organizations and individuals must place paramount focus on risk assessment and management, implement comprehensive security controls, nurture a culture of security awareness and training, and stand ready with well-defined incident response and recovery strategies. By anchoring their cybersecurity strategy on these four pillars of digital transformation, organizations and individuals are empowered to minimize the impact of cyberattacks when adversity strikes.

Opportunities and Challenges in Cybersecurity in the Digital Age
Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field that presents both opportunities and challenges.
Opportunities in Cybersecurity in the Digital Age
1. Increased Demand for Cybersecurity Professionals: As cyberattacks become more frequent and sophisticated, the demand for cybersecurity professionals is on the rise. This presents an opportunity for individuals with cybersecurity skills to pursue a rewarding career in this field.
2. Advancements in Technology: Advancements in technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, can help improve cybersecurity measures by detecting and responding to threats more quickly and accurately.
3. Increased Awareness: As cyberattacks become more prevalent, individuals and organizations are becoming more aware of the importance of cybersecurity. This increased awareness can help drive investment in cybersecurity measures.
Challenges in Cybersecurity in the Digital Age
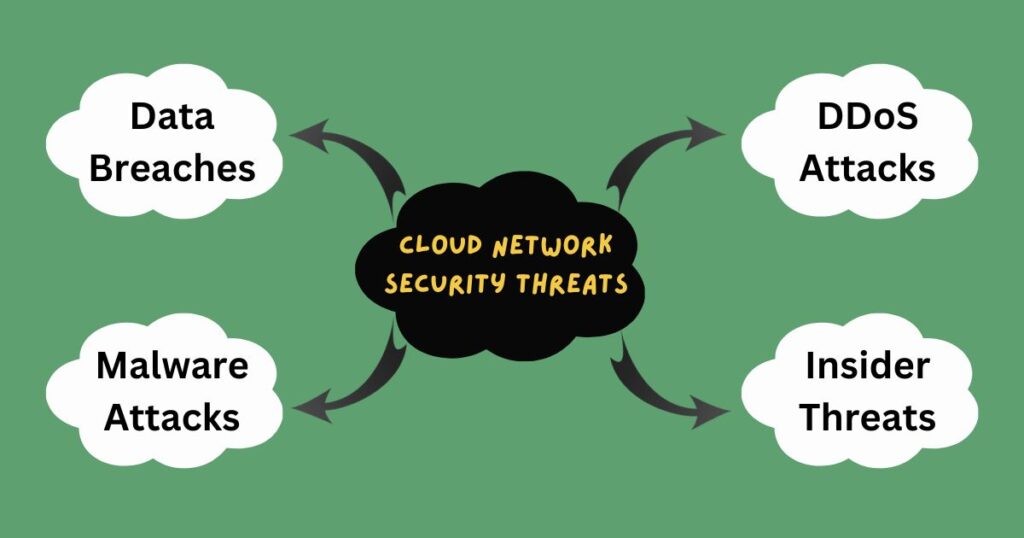
1. Sophisticated Cyber Threats: Cybercriminals are constantly discovering new attack vectors, making it challenging for organizations to keep up with the latest threats. Ransomware attacks, phishing scams, and data breaches are just some of the challenges that organizations face.
2. Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals: The demand for cybersecurity professionals is on the rise, but there needs to be more skilled professionals to fill these roles. This shortage makes it challenging for organizations to implement adequate cybersecurity measures.
3. Complexity of IT Infrastructure: The increasing complexity of IT infrastructure, including cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT), makes it challenging to manage security across all devices and platforms.
Common Types of Cyberattacks on Individuals

Cyberattacks can take many forms, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated ransomware attacks. Here are some examples of common types of cyberattacks on individuals:
1. Phishing Scams: Phishing scams are fraudulent emails or messages that trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords or credit card numbers.
2. Malware Attacks: Malware is a type of software that is designed to harm a computer system or network. Malware attacks can be caused by worms, Trojan horses, and viruses, among other things.
3. Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts an individual’s data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key.
4. Identity Theft: Identity theft occurs when an individual’s personal information is stolen and used for fraudulent purposes.
5. Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: MitM attacks occur when an attacker intercepts communication between two parties to steal sensitive information.
These are just a few examples of the many types of cyberattacks that individuals face. To protect against these threats, individuals must implement strong cybersecurity measures that safeguard against a wide range of threats, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated ransomware attacks.
How Can Individuals Improve Their Personal Cybersecurity?

In the era of cybersecurity in the Digital Age, enhancing personal cybersecurity is imperative to safeguard your personal information and sensitive data from the ever-present cyber threats. This guide outlines several steps individuals can take to bolster their personal cybersecurity:
- Keep Software Up to Date: Ensure that all software and operating systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Use Antivirus Software: Install and regularly update antivirus software to detect and remove malware.
- Implement Access Controls: Implement access controls to limit the number of users who have administrative privileges.
- Train Employees: Train employees on how to identify and avoid phishing scams and other social engineering tactics used by cybercriminals.
- Back-Up Data Regularly: Regularly back up important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
- Use Strong Passwords: Use strong passwords that are difficult to guess and change them regularly.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
Think Before You Click or Share: Do not click on links or open attachments from unwanted messages or emails. If you do, it could result in the installation of spyware on your computer. Be careful when communicating Personally Identifiable Information (PII) via phone, text message, or email, particularly when you are not the one initiating the conversation. Limit the amount of information you divulge on social media and adjust the privacy settings of your accounts.
By implementing these measures, individuals can minimize the risk of cyberattacks and protect their sensitive data.
Cybersecurity Challenges Faced by Organizations
In the realm of cybersecurity in the digital age, organizations grapple with evolving challenges as the digital landscape expands. Protecting sensitive data and ensuring digital operations’ integrity is paramount. Understanding and addressing these cybersecurity challenges faced by organizations is critical to fortifying their digital infrastructure’s security and resilience. Here are some key challenges:
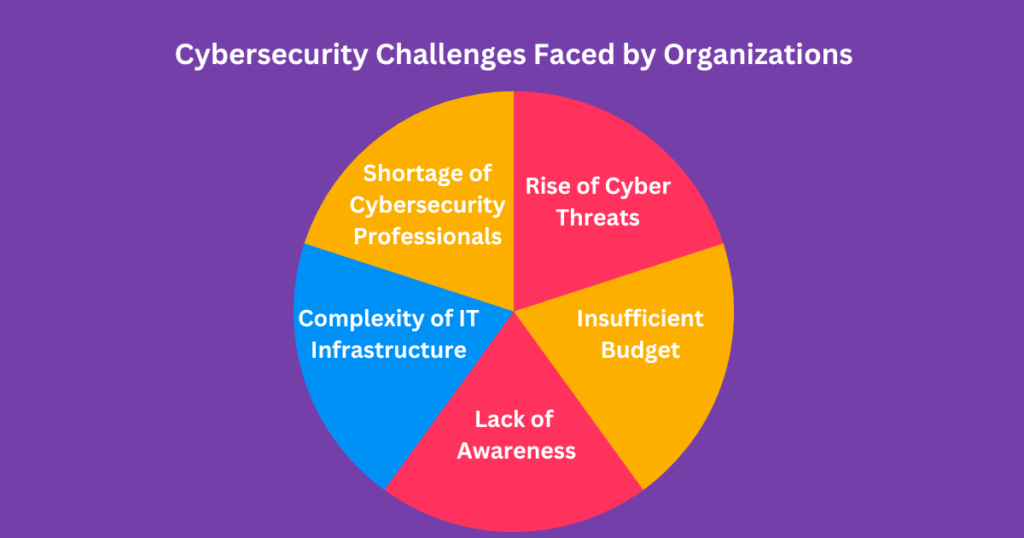
1. Rise of Cyber Threats: As technology evolves, cyberattacks are becoming more complex and destructive. Cyberattacks on information systems, as well as cyber espionage, are just a few of the issues organizations have to contend with. Cybercriminals are constantly discovering new attack methods, which require ongoing improvements in security techniques.
2. Shortage of Cybersecurity Professionals: The demand for cybersecurity professionals is on the rise, but there needs to be more skilled professionals to fill these roles. This shortage makes it challenging for organizations to implement adequate cybersecurity measures.
3. Complexity of IT Infrastructure: The increasing complexity of IT infrastructure, including cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT), makes it challenging to manage security across all devices and platforms.
4. Lack of Awareness: Many organizations need more awareness about the importance of cybersecurity and the risks associated with cyberattacks. This lack of understanding can lead to inadequate investment in cybersecurity measures and a lack of preparedness for cyberattacks.
5. Insufficient Budget: Cybersecurity measures require significant investment in technology, personnel, and training. Many organizations struggle to allocate a sufficient budget for cybersecurity measures, which can lead to inadequate protection against cyber threats.
To address these challenges in the digital age, organizations must implement strong cybersecurity measures that safeguard against various threats, from simple computer viruses to sophisticated ransomware attacks. In this era of “cybersecurity in the digital age,” cybersecurity professionals utilize various technologies and best practices, such as advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation, to fortify their defenses. In addition to these domains, organizations must also emphasize risk assessment and management, security control implementation, security awareness and training, and incident response and recovery. By incorporating these four pillars into an effective cybersecurity strategy for the digital age, organizations can minimize the impact of cyberattacks when they occur.
Examples of Cyberattacks on Organizations
Cyberattacks can take many forms, from simple phishing scams to sophisticated ransomware attacks. Here are some examples of cyberattacks on organizations:
- Ransomware Attacks: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts an organization’s data and demands payment in exchange for the decryption key. In 2021, Electronic Arts, one of the world’s biggest video game publishers, was breached by hackers who stole source code used in company games.
- Data Breaches: Data breaches occur when an organization’s sensitive data is accessed or stolen by unauthorized individuals. In 2021, McDonald’s suffered a data breach that exposed the private information of customers and employees in South Korea and Taiwan.
- Phishing Scams: Phishing scams are fraudulent emails or messages that trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords or credit card numbers. In 2021, Peloton announced that it was targeted by hackers who stole customer data through a phishing scam.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: DoS attacks occur when an organization’s servers are overwhelmed with traffic, causing them to crash or become unavailable. In 2021, Amazon Web Services (AWS) experienced a DoS attack that caused widespread outages across the internet.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are long-term targeted attacks that aim to steal sensitive information from an organization. In 2021, the Russian hacking group APT29 was accused of targeting organizations involved in COVID-19 vaccine development.
These are just a few examples of the many types of cyberattacks that organizations face. To protect against these threats, organizations must implement strong cybersecurity measures that safeguard against various threats, from simple computer viruses to sophisticated ransomware attacks. Cybersecurity professionals use a variety of technologies and best practices to protect against these threats, including advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation.
How Can Organizations Protect Against Ransomware Attacks?
In the realm of cybersecurity in the digital age, organizations can take several steps to protect against ransomware attacks:
1. Keep Software Up to Date: Ensure that all software and operating systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
2. Use Antivirus Software: Install and regularly update antivirus software to identify and eliminate malware.
3. Implement Access Controls: Implement access controls to limit the number of users who have administrative privileges.
4. Train Employees: Train employees on how to identify and avoid phishing scams and other social engineering tactics used by cybercriminals.
5. Back-Up Data Regularly: Regularly back up important data to an external hard drive or cloud storage service.
6. Use Strong Passwords: Use strong passwords that are difficult to guess and change them regularly.
7. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security to user accounts.
8. Conduct Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in the organization’s IT infrastructure.
By implementing these measures, organizations can minimize the risk of ransomware attacks and protect their sensitive data.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is an essential practice that helps protect individuals and organizations from cybercrime. In the digital age, cybersecurity has become more critical than ever before as cyberattacks have become more sophisticated and frequent. To ensure effective cybersecurity, individuals and organizations must implement strong cybersecurity measures that safeguard against various threats, from simple computer viruses to sophisticated ransomware attacks. Cybersecurity professionals use various technologies and best practices to protect against these threats, including advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and automation.