Innovations in agriculture like precision culture, GMOs, vertical farming, aquaponics, and agricultural drones are reshaping farms, promising unprecedented efficiency, sustainability, and productivity. Imagine drones surveying crops, robots nurturing vertical gardens, and AI algorithms safeguarding harvests. These aren’t futuristic visions, but tangible tools transforming the way we feed the world.
With fewer resources and less environmental impact, these innovations have the potential to nourish both bodies and the planet. The challenges are real, but the rewards are transformative. Let’s embrace this exciting journey—the journey of innovations in agriculture.
Precision Agriculture: Optimising Resource Use
Precision agriculture, also known as smart farming/ satellite farming, encompasses a suite of technologies that enable farmers to make data-driven decisions to optimise resource use and maximise crop yields. It’s a farming management concept/ science that uses technology to improve crop yields and management decisions.

Critical management decisions hinge on the data points furnished by precision agriculture, with a profound impact on various facets of farmland and agricultural output, notably:
- Resource use efficiency
- Sustainability
- Profitability
- Productivity
- Quality
This avant-garde agricultural technology leverages big data to empower management decisions, granting farmers the capability to regulate variables affecting crop yields, such as moisture levels, soil conditions, and microclimates, ultimately maximising output.
Its implementation relies on cutting-edge technologies like remote sensing systems, drones, robotics, and automation, fostering improved crop health and the optimal utilization of agricultural resources, resulting in heightened productivity.
According to Grand View Research, the global precision farming market is anticipated to reach $16.35 billion by 2028, displaying a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 13.1%. The organisation posits that increasing governmental backing and rising demand for efficient crop health monitoring will be instrumental in propelling market growth. Now, we will talk about GMOs.
Genetically Modified Crops: One of the Pioneering Innovations in Agriculture
Genetically modified crops (GMOs), also known as genetically engineered (GE) crops, have emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing agricultural productivity and addressing global food security challenges.

An animal, plant, or microorganism that has had its DNA altered by genetic engineering is known as a genetically modified organism (GMO).By introducing specific genetic traits into plants, scientists have developed crops with remarkable resilience to pests, diseases, and harsh environmental conditions, leading to reduced crop losses and increased yields.
Additionally, GMOs have been instrumental in improving the nutritional value of crops, addressing micronutrient deficiencies in vulnerable populations, and reducing the allergenicity of certain foods.
The Power of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering provides a powerful tool that enhances agricultural productivity. By modifying the genetic makeup of crops, scientists can optimise their characteristics and improve their ability to thrive in various environmental conditions. This technology has the potential to revolutionise farming practises and lead to more sustainable and resilient food production systems.
Enhancing Pest and Disease Resistance
One of the most significant contributions of GMOs lies in their ability to confer resistance to pests and diseases, which are major causes of crop losses worldwide. By introducing genes from other organisms or synthesizing novel genes, scientists have developed crops that are naturally resistant to specific pests and diseases.
For instance, Bt cotton, engineered with a gene from the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis, produces a protein that is toxic to certain insects, reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and promoting sustainable pest management practices.
Similarly, Golden Rice, fortified with beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, has been developed to address vitamin A deficiency, a leading cause of blindness in children in developing countries.
Improving Nutritional Value
GMOs have also played a crucial role in enhancing the nutritional value of crops, particularly targeting micronutrient deficiencies that affect millions of people worldwide. Golden Rice, as mentioned earlier, is a prime example of this application.
Additionally, scientists have developed iron-rich rice, iron-biofortified beans, and high-protein maize, addressing iron deficiency anemia and protein malnutrition, respectively. These nutrient-enriched crops have the potential to significantly improve the health and well-being of populations in developing countries.
Reducing Allergenicity
GMOs have also been used to reduce the allergenicity of certain foods, making them more accessible to individuals with allergies. For instance, soybeans have been modified to reduce the levels of glycinin and beta-conglycinin, the two major allergenic proteins in soybeans, enabling individuals with soy allergies to enjoy soy-based products.
Additionally, researchers are working on developing hypoallergenic peanuts, which could revolutionize the lives of peanut-allergic individuals.
Addressing Public Concerns and Ensuring Safety
Despite the undeniable benefits of GMOs, their development and use have been accompanied by public concerns and debates surrounding potential risks to human health and the environment. These concerns have primarily focused on the potential for unintended effects on non-target organisms, the potential for gene transfer to wild plants, and the potential impact on biodiversity.
To address these concerns, comprehensive regulatory frameworks have been established in many countries to ensure the safety of GMOs.
These frameworks mandate rigorous scientific assessments of GMOs prior to their commercialization, evaluating potential risks and ensuring that they meet safety standards for human health and the environment. Additionally, ongoing research continues to address potential long-term effects and refine risk assessment methodologies.
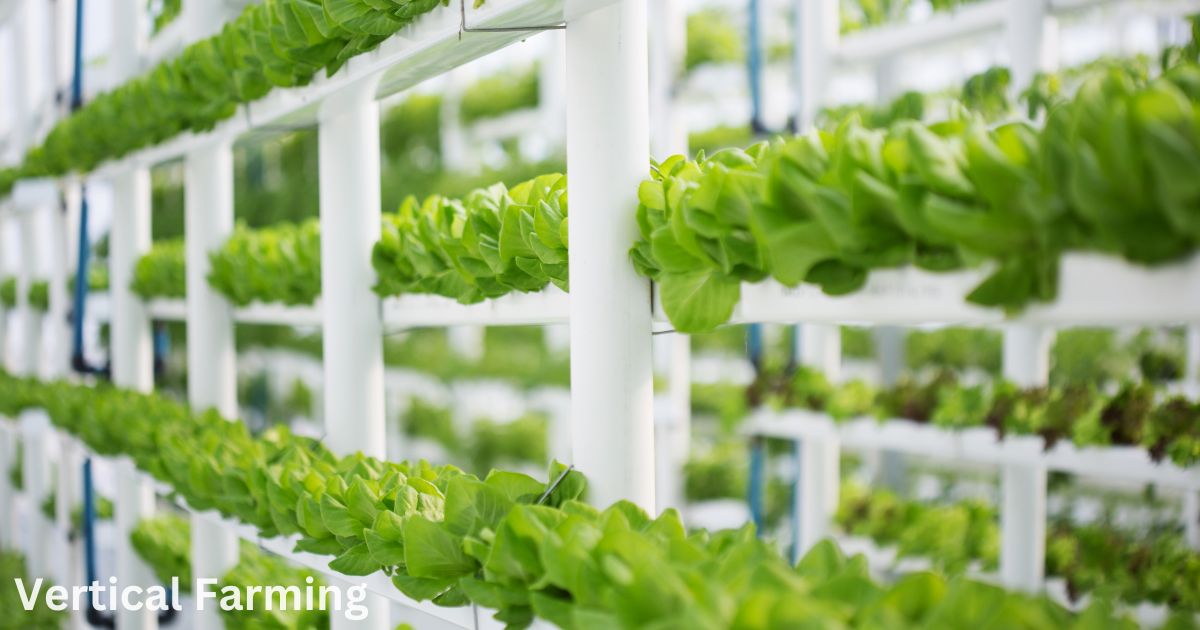
Vertical Farming: Cultivating Crops in Controlled Environments
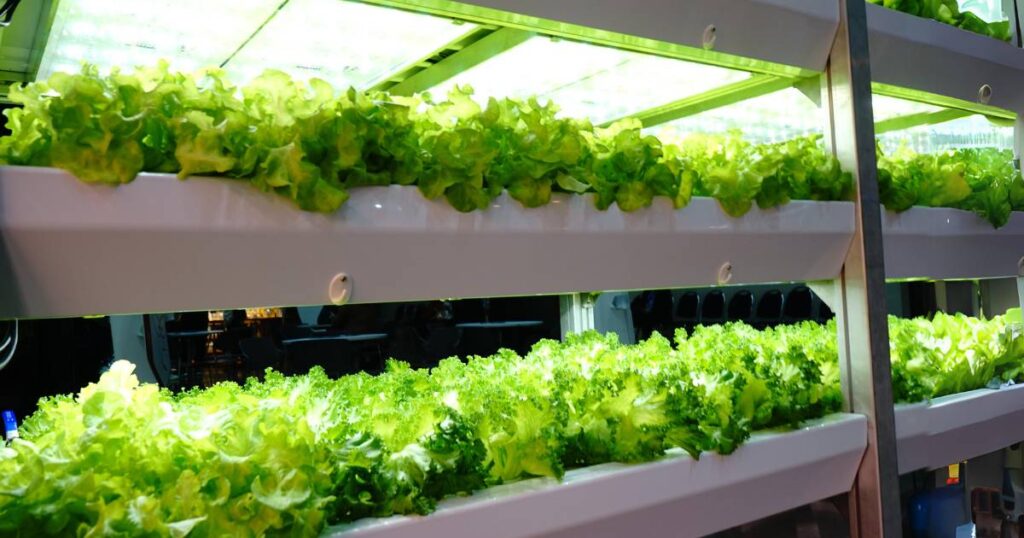

As the global population continues to grow and land availability becomes increasingly limited, traditional farming methods face challenges in meeting the rising demand for food. Vertical farming has emerged as a promising solution, offering a transformative approach to agriculture that utilizes vertically stacked layers or indoor spaces to cultivate crops. This innovative technique has gained traction as a sustainable and efficient method for urban agriculture, year-round production, and the cultivation of specialty crops.
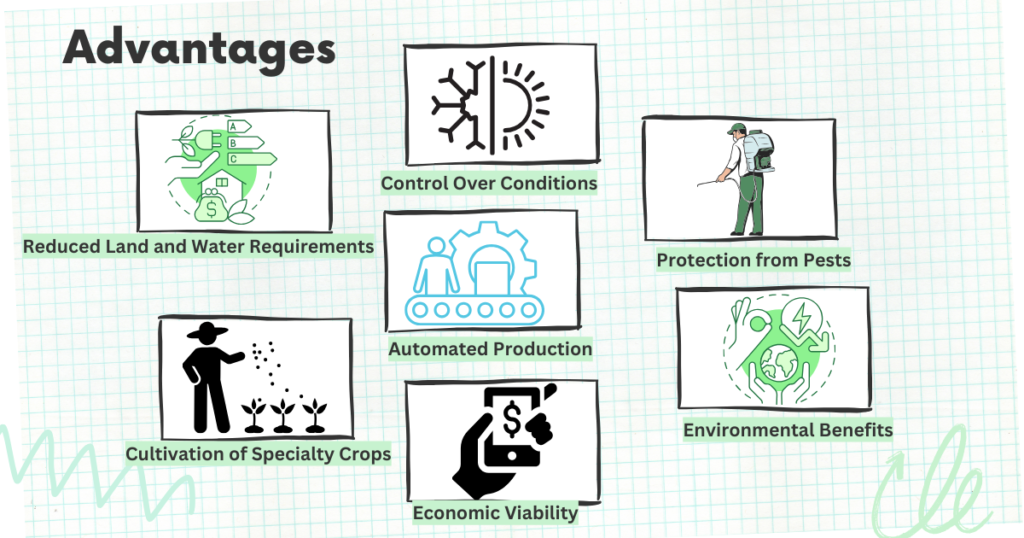
Vertical farming systems offer a multitude of advantages over traditional farming methods, making them a compelling alternative to modern agriculture:
Reduced Land and Water Requirements
Unlike traditional farming, which requires vast expanses of land, vertical farming systems can be established in urban areas, utilising rooftops, warehouses, or dedicated vertical farm structures. This significantly reduces the land footprint required for crop production, making it a viable option for urban environments where land is scarce.
Additionally, vertical farming systems employ hydroponic or aeroponic techniques, which conserve water by delivering nutrients directly to plant roots through nutrient-rich solutions or misting systems. This results in significantly reduced water consumption compared to traditional farming methods that rely on rainfall or irrigation systems.
Improved Control Over Growing Conditions
Vertical farming systems provide growers with unprecedented control over the environment in which their crops are grown. This includes precise control over temperature, humidity, light intensity, and nutrient levels, allowing for optimal growth conditions that maximize yield and quality. By eliminating the unpredictable factors of outdoor weather and pests, vertical farming ensures a consistent and reliable supply of high-quality crops throughout the year.
Protection from Pests and Diseases
Vertical farming systems offer a closed environment that is isolated from external pests and diseases, eliminating the need for harsh chemical pesticides and herbicides. This results in cleaner, healthier crops that are free from harmful residues. Additionally, the controlled environment allows for the implementation of integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, utilizing natural pest control methods to maintain a healthy crop ecosystem.
Automated and Efficient Production
Vertical farming systems can be highly automated, minimizing labor costs and maximizing production efficiency. Automated systems can handle tasks such as seeding, transplanting, nutrient delivery, pest control, and harvesting, reducing the need for manual labor. This automation, coupled with the controlled environment and efficient use of space, allows vertical farming operations to achieve higher yields per square foot compared to traditional farming methods.
Cultivation of Specialty Crops
Vertical farming is particularly well-suited for the cultivation of specialty crops, such as herbs, leafy greens, and berries. These crops thrive in the controlled environments of vertical farms, and their shorter growth cycles allow for multiple harvests per year. Additionally, vertical farming can be used to grow crops that are difficult or impossible to cultivate in traditional outdoor settings, such as crops requiring specific temperature or humidity conditions.
Environmental Benefits
Vertical farming offers several environmental benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, minimized soil degradation, and improved water conservation. By reducing the need for transportation and refrigeration, vertical farming contributes to a lower carbon footprint for food production. Additionally, the controlled environment and hydroponic systems eliminate soil erosion and contamination, protecting soil health and reducing the impact on surrounding ecosystems.
Economic Viability
While the initial investment in vertical farming infrastructure can be higher than traditional farming, the long-term economic benefits are promising. Vertical farming’s efficient use of space, high yields, and year-round production can lead to increased profitability and a shorter return on investment. Additionally, vertical farming can create new jobs in urban areas, stimulating local economies and contributing to community development.
Future of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is still in its early stages of development, but it holds immense potential to revolutionize the way we grow food in the future. As technology advances and costs continue to decline, vertical farming is expected to become increasingly widespread, particularly in urban areas and for the cultivation of high-value crops. The combination of improved efficiency, environmental sustainability, and year-round production makes vertical farming a promising solution for addressing the growing challenges of food security and resource scarcity in a changing world.
Aquaponics: Creating Sustainable Food Production Systems
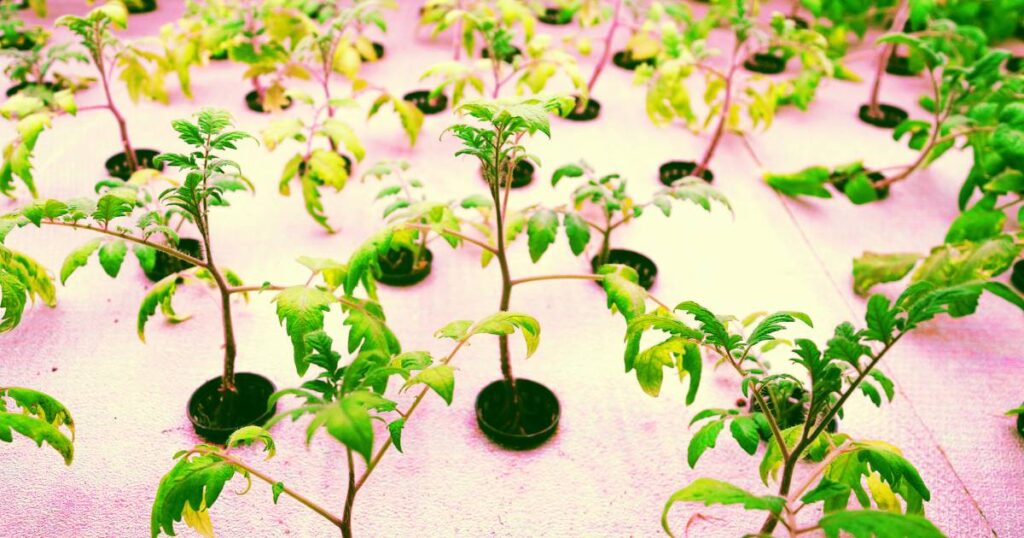

Aquaponics is not just a buzzword in the world of sustainable agriculture; it represents a groundbreaking approach to food production that holds immense potential for our future. By combining aquaculture and hydroponics, this innovative method enables us to cultivate both fish and plants in a symbiotic environment, fostering a self-sustaining ecosystem that significantly reduces water usage and eliminates the need for harmful chemicals.
The benefits of aquaponics are truly remarkable. Firstly, it allows us to grow more food in less space compared to traditional farming methods. By utilizing vertical farming techniques, we can maximize productivity while minimizing land requirements. This is particularly crucial as our population continues to grow, placing increasing pressure on our agricultural resources.
Moreover, aquaponics offers a sustainable solution to water scarcity issues. Unlike conventional farming practices that consume vast amounts of water, aquaponic systems recycle and reuse water within the closed-loop system. By leveraging the natural filtration provided by fish waste, plants receive essential nutrients while purifying the water for the aquatic organisms—an elegant cycle that conserves this precious resource.
In addition to its environmental advantages, aquaponics also presents economic opportunities for farmers and entrepreneurs. The high yield potential coupled with reduced operating costs make it an attractive option for commercial-scale agriculture ventures. Furthermore, by cultivating fresh produce locally and year-round regardless of climate conditions, aquaponics contributes to food security and resilience against external disruptions.
It is important to note that while aquaponics requires careful monitoring and management, advancements in technology have made it increasingly accessible even for novice farmers or urban gardeners. With automated monitoring systems and user-friendly designs available on the market today, anyone can embark on their journey towards sustainable food production.
Aquaponics represents a game-changing solution in our quest for sustainable agriculture. By harnessing nature’s intricate balance between fish and plants within a closed-loop ecosystem, we can cultivate abundant crops while safeguarding our environment and natural resources. As we face mounting challenges in food security and environmental conservation, embracing aquaponics is a step towards a brighter future for all.
Agricultural Drones: Your Wingmen in Crop Monitoring and Management
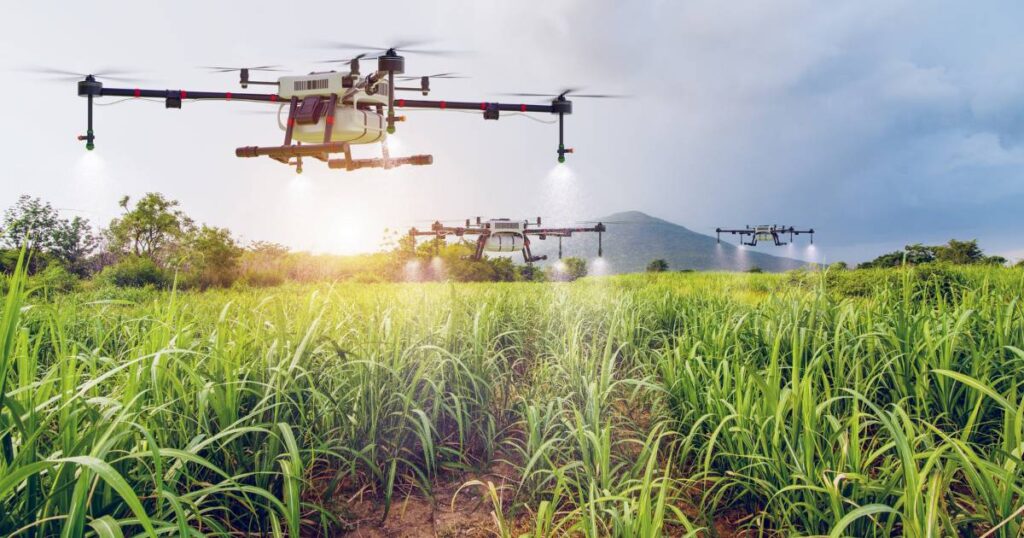

Imagine soaring above your fields, gaining a bird’s-eye view of your crops’ health and condition. This isn’t a scene from a futuristic sci-fi movie; it’s a reality thanks to the revolutionary technology of agricultural drones. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are equipped with specialized sensors and cameras, providing farmers with invaluable insights that are transforming the way we monitor and manage crops.
Optimizing Resources Like a Pro
Agricultural drones act like your eyes in the sky, delivering real-time data on your crops’ health. This allows you to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest control with laser-sharp precision. Instead of treating entire fields uniformly, you can target areas that need attention, saving time, minimizing waste, and maximizing crop production.
Boosting Yields to New Heights
Drones are your allies in the quest for increased yields. They capture high-resolution images, revealing issues like nutrient deficiencies or diseases before they spread. This early detection empowers you to take swift action and mitigate potential damage, resulting in healthier plants and bountiful harvests.
Saving Money, Smartly
Gone are the days of expensive manned aircrafts and time-consuming manual labor for crop monitoring. Agricultural drones offer a cost-effective solution, covering large areas quickly and efficiently while collecting accurate data on plant health. This significant reduction in human involvement and equipment costs allows you to save valuable resources and reinvest them in other areas of your farm.
Minimizing Environmental Impact, Naturally
Agricultural drones are not only good for your pocket; they’re also good for the planet. Their precise data collection allows you to pinpoint specific areas that require attention, reducing the need for large-scale chemical applications. This targeted approach minimizes the use of pesticides and fertilizers, protecting the environment and promoting sustainable farming practices.
The Impact of Agricultural Innovations
The impact of agricultural innovations is far-reaching, extending beyond increased food production and reduced environmental impact. These advancements have the potential to:
- Improve food security: By enhancing productivity and reducing crop losses, agricultural innovations can help ensure a stable food supply for a growing population.
- Promote sustainable agriculture: Precision agriculture and vertical farming techniques can reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture, minimizing water consumption, pesticide use, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Empower smallholder farmers: Access to affordable and appropriate technologies can empower smallholder farmers in developing countries to improve their livelihoods and enhance food security in their communities.
- Create new jobs and opportunities: The development and adoption of agricultural technologies are creating new jobs in areas such as data analytics, robotics, and vertical farming.
As the global population continues to grow and the demand for food increases, agricultural innovations will play a crucial role in ensuring a sustainable and secure food supply for future generations. By embracing these advancements, we can cultivate a more productive, environmentally friendly, and resilient agricultural system that nourishes the world.
In summary, the era of New Innovations in Agriculture ushers in transformative changes with cutting-edge technology. From Precision Agriculture’s data-driven decisions to optimize resources, to the power of Genetically Modified Crops in enhancing productivity and addressing food security, each innovation plays a crucial role.
Aquaponics, a fusion of aquaculture and hydroponics, stands out for growing more food in less space while addressing water scarcity sustainably. Each innovation, though in its early stages, holds immense potential to revolutionize agriculture, addressing the growing challenges of food security and resource scarcity in a changing world.