In the fast-paced world of technology and innovation, few sectors have undergone as radical a transformation as the textile industry. What innovation changed the textile industry?
In this article, we will discuss in detail the innovations that altered the very fabric of the textile world. Let’s embark on a journey through time, exploring the profound impact of various innovations that have reshaped the fabric of the textile world.
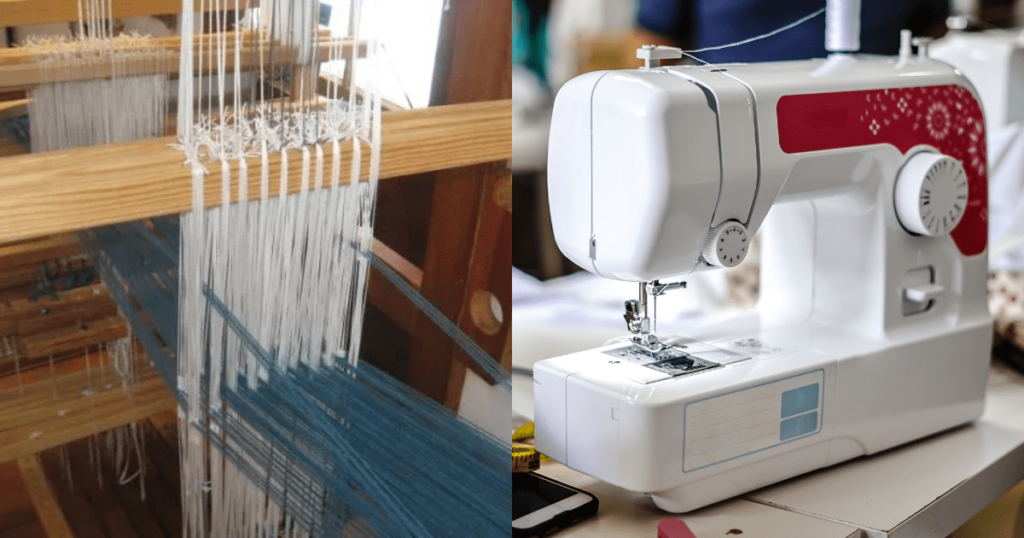

The textile industry, a cornerstone of human civilization, has evolved significantly over the years. From ancient manual weaving to the modern, automated production lines, innovation has been the driving force behind these transformative changes. how are smart textile innovation influencing the functionality of clothing.
The Technological Revolution: A Turning Point
The advent of technology marked a turning point in human history, ushering in an era of unprecedented progress and change. But what innovation changed the textile industry during this revolution? This transformative era was driven by a series of groundbreaking inventions and innovations that transformed nearly every aspect of society, from manufacturing and transportation to communication and agriculture
- The Textile Industry: A Catalyst for Change: The textile industry was one of the first sectors to be revolutionized by technology. The invention of the flying shuttle in 1733 and the spinning jenny in 1764 dramatically increased the speed and efficiency of textile production. These machines, powered by water or steam, could produce far more yarn and cloth than traditional hand looms, leading to a surge in output and a decline in labor costs.
- The Rise of Mechanized Production: The mechanization of textile production had a profound impact on the industry. It led to the establishment of large-scale factories, where machines performed tasks that were once done by hand. This shift from manual labor to mechanized production resulted in significant gains in productivity and efficiency.
- The Impact on Society: The technological revolution in the textile industry had far-reaching consequences for society. It led to the urbanization of many workers, as people moved from rural areas to cities to work in factories. This shift also contributed to the growth of the middle class, as factory workers were able to earn higher wages than their agricultural counterparts.
Introduction of Automation: What Innovation Changed the Textile Industry

Automation is an innovative form of mechanization that uses current technology and automated machinery to produce more products in a factory in a shorter amount of time and with more efficiency. The introduction of automation in the textile industry marked a paradigm shift, fundamentally altering the way fabrics were produced. Machines, once considered mere tools, evolved into capable partners, taking over repetitive tasks and allowing human workers to focus on more intricate aspects of production. This transformation revolutionized the industry, enhancing efficiency, precision, and overall productivity.
Replacing Repetitive Tasks with Machine Precision: Textile production has long been characterized by repetitive tasks, such as spinning, weaving, and sewing. These tasks, while essential, were often tedious and time-consuming, requiring workers to perform the same motions countless times. Automation addressed this challenge by replacing these repetitive tasks with machines.

Spinning: From Spindle to Automation: Spinning, the process of converting raw fibers into yarn, was one of the first areas to experience automation. The introduction of spinning machines, such as the spinning jenny and the water frame, dramatically increased the speed and efficiency of yarn production. These machines could spin multiple strands of yarn simultaneously, significantly reducing the time and labor required for this crucial step.
Weaving: From Hand Looms to Power Looms: Weaving, the process of interlacing yarns to create fabric, underwent a similar transformation. The invention of power looms, such as the flying shuttle and the power loom, mechanised the weaving process, replacing the slow and laborious hand looms. These machines could weave complex patterns much faster and with greater precision, leading to a surge in fabric production.
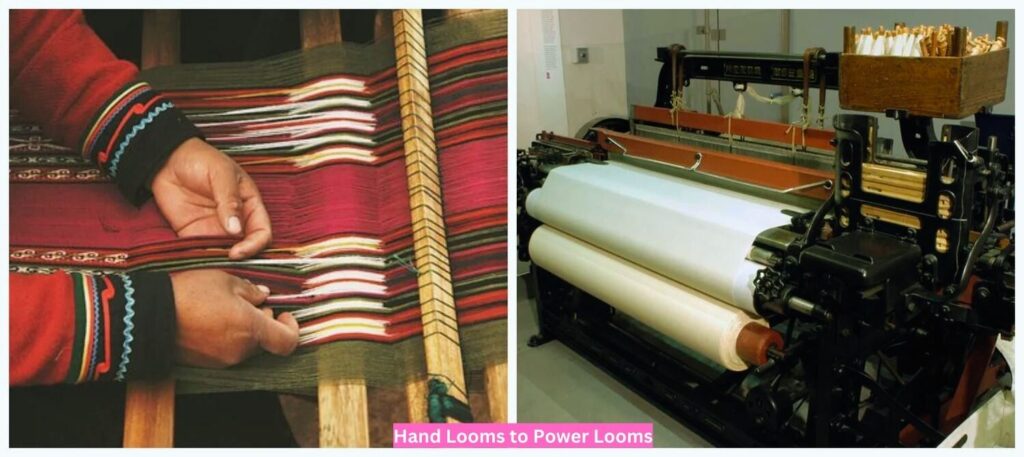

Sewing: From Needle and Thread to Automated Machines: Sewing, the process of joining fabric pieces to create garments or other textile products, also benefited from automation. The introduction of sewing machines, such as the Singer sewing machine, revolutionized the garment industry. These machines could perform precise stitches at high speeds, significantly reducing the time and labor required for sewing.

Human Workers: From Task Performers to Skilled Overseers: With machines taking over repetitive tasks, human workers transitioned from mere task performers to skilled overseers. They focused on monitoring the machines, ensuring their proper functioning, and making adjustments as needed. They also took on more intricate tasks, such as designing patterns, inspecting fabric quality, and troubleshooting complex production issues.
Nanotechnology in Textiles: A Revolution in the Fabric of Our World
The textile industry, spanning centuries of innovation, has witnessed a remarkable transformation with the advent of nanotechnology. This cutting-edge technology, operating at the scale of billionths of a meter, has revolutionized the way we create, enhance, and utilize fabrics, introducing a paradigm shift in the production of clothing, healthcare textiles, and beyond.

Nanoparticles: The Building Blocks of Textile Transformation: Nanoparticles, the heart of nanotechnology, are minuscule particles ranging in size from 1 to 100 nanometers, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. Their incredibly small size endows them with unique properties that have far-reaching implications for the textile industry.
Enhanced Durability: Protecting Fabrics Against Wear and Tear: One of the key benefits of nanotechnology in textiles is the enhancement of durability. By incorporating nanoparticles into fabrics, textile scientists have created materials that are resistant to abrasion, wear, and tear. This improved durability extends the lifespan of garments, reducing the environmental impact of textile waste.
Water Repellency: Keeping Fabrics Dry and Comfortable: Nanoparticles have also revolutionized water repellency in textiles. By applying nanoparticle coatings, fabrics can be treated to repel water, preventing stains and keeping garments dry in wet conditions. This technology is particularly valuable for outdoor apparel and sportswear, ensuring comfort and performance in challenging environments.
Antibacterial Properties: Promoting Hygiene and Health: Nanotechnology has also introduced antibacterial properties into textiles, offering protection against microbes and preventing the spread of infections. Nanoparticles embedded in fabrics can inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and viruses, promoting hygiene and reducing the risk of contamination. This technology is particularly relevant for healthcare textiles, such as surgical gowns and patient linens.
Self-Cleaning Fabrics: Minimizing Maintenance and Environmental Impact: The self-cleaning properties of nanotechnology-enhanced textiles are a significant advancement. By incorporating nanoparticles, fabrics can be engineered to repel dirt, dust, and stains, minimizing the need for frequent washing and reducing the environmental impact of textile cleaning. This technology holds promise for everyday wear and outdoor apparel, promoting sustainability and convenience.
Smart Textiles: Integrating Intelligence into Fabrics: Nanotechnology is also paving the way for smart textiles, integrating intelligence and functionality into fabrics. By incorporating sensors, conductors, and other nanomaterials, textiles can respond to external stimuli, such as temperature, light, and pressure. These smart textiles have the potential to monitor health vitals, enhance athletic performance, and provide personalized comfort.
Read More: Nanotechnology in Smart Textiles
Artificial Intelligence in Textile Design: A Creative Force and Production Optimizer
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming the world around us, and the textile industry is no exception. While AI is often associated with complex calculations and automation, it is also proving to be a valuable tool for textile designers, enhancing creativity, streamlining production processes, and ushering in a new era of innovation in the textile industry.
AI as a Creative Partner: Enhancing Design Inspiration and Possibilities: AI is not just about replacing human creativity; it’s about augmenting it. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of existing designs, patterns, and trends to identify patterns, predict future trends, and generate new and innovative design ideas. This allows designers to explore new creative avenues, experiment with unconventional combinations, and break free from traditional design boundaries.
For instance, AI-powered design tools can generate a variety of patterns based on a designer’s initial sketch or color palette, providing a wealth of options to explore and refine. Additionally, AI can analyze fashion trends and consumer preferences to inform design decisions, ensuring that designs are not only aesthetically pleasing but also align with current market demands.
Optimizing Production Processes: Streamlining Efficiency and Reducing Waste: AI is also transforming the back-end of textile production, optimizing processes, reducing waste, and enhancing overall efficiency. AI algorithms can analyze production data to identify bottlenecks, predict machine downtime, and optimize production schedules. This data-driven approach can significantly reduce production costs, minimize downtime, and ensure that production lines operate at peak efficiency.
AI also plays a crucial role in waste reduction. By analyzing patterns and fabric usage, AI can optimize cutting patterns to minimize fabric waste. Additionally, AI-powered defect detection systems can identify flaws in fabrics early in the production process, preventing them from reaching the final product and reducing the need for rework.
The Future of AI in Textile Design: A Symbiosis of Creativity and Technology: The integration of AI into textile design is still in its early stages, but the potential is immense. As AI algorithms become more sophisticated and data sets expand, AI will continue to play an increasingly important role in both the creative and technical aspects of textile design.
AI will not replace human designers; it will empower them. Designers will increasingly rely on AI as a creative partner, leveraging its ability to analyze trends, generate new ideas, and optimize production processes. This symbiosis of creativity and technology will lead to the creation of innovative, sustainable, and aesthetically pleasing textiles that meet the demands of a rapidly changing world.
3D Printing in Textiles: A Revolution in Fabrication
The textile industry, with its rich history of innovation and craftsmanship, is undergoing a transformative shift with the advent of 3D printing. This technology, which has revolutionized various industries, is now making its mark on the world of textiles, offering unprecedented design possibilities, enhanced efficiency, and a paradigm shift in textile production.
From Traditional Techniques to Digital Fabrication: Traditional textile manufacturing methods, while rooted in time-honored techniques, often face limitations in terms of design complexity and production speed. 3D printing, on the other hand, breaks free from these constraints, allowing for the creation of intricate designs, customized products, and seamless production processes.
Unleashing Design Freedom: Intricate Structures and Customized Creations: 3D printing empowers textile designers to explore the full spectrum of their creativity. Unlike traditional methods that are restricted by the limitations of weaving or knitting, 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries, intricate structures, and even embedded functionalities within textiles. This design freedom opens up a world of possibilities for innovative products, from customized apparel to architectural textiles with integrated structures.
Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined Production and Reduced Waste: 3D printing also revolutionizes the production process, streamlining operations and reducing waste. Unlike traditional methods that require cutting, sewing, and assembling multiple pieces, 3D printing can create a complete textile product in a single step. This additive manufacturing approach minimizes waste, reduces labor costs, and streamlines production, leading to shorter lead times and increased efficiency.
Sustainable Textile Production: Minimizing Environmental Impact: As the textile industry faces increasing scrutiny for its environmental impact, 3D printing offers a promising path towards sustainability. By reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and enabling on-demand production, 3D printing can significantly lower the environmental footprint of textile manufacturing.
Applications of 3D Printing in Textiles: A Diverse Spectrum
The applications of 3D printing in textiles span a wide range, from fashion and sportswear to footwear, home textiles, and industrial applications.
- Fashion and Sportswear: 3D printing is transforming the fashion industry, enabling the creation of customized apparel, intricate designs, and personalized fit. It is also revolutionizing sportswear, producing performance wear with integrated functionalities and enhanced comfort.
- Footwear: 3D printing is disrupting the footwear industry, allowing for the creation of customized shoes, personalized midsoles, and innovative designs. It is also enabling the production of lightweight, durable, and comfortable footwear.

- Home Textiles: 3D printing is making its mark on home textiles, creating customized décor items, intricate patterns, and functional textiles with integrated lighting or sensors. It is also paving the way for personalized bedding and home furnishings.
- Industrial Applications: 3D printing is finding applications in industrial textiles, producing filters for filtration systems, medical textiles with embedded sensors, and protective textiles with enhanced properties.
The Future of 3D Printing in Textiles: A World of Possibilities
As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, its impact on the textile industry is bound to expand. With advancements in material science, printing speed, and resolution, 3D printing will further revolutionize textile design, production, and sustainability.
In the future, we can envision a world where 3D printing is seamlessly integrated into the textile industry, enabling the creation of highly customized, efficient, and sustainable textiles that enhance our lives and shape the future of fashion and design.
Robotics in Textile Factories: A Transformation in Precision and Output
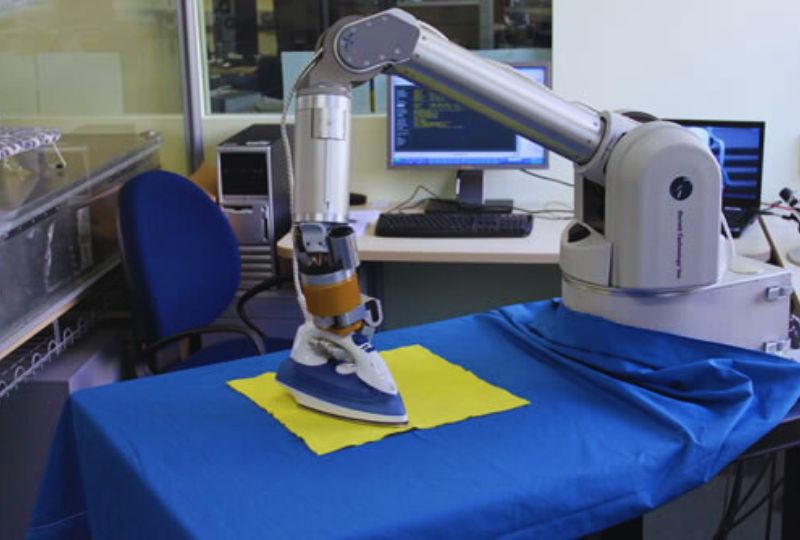

The textile industry, a cornerstone of human civilization, is undergoing a remarkable transformation driven by the integration of robotics. Automation, once confined to stand-alone machines, has evolved into sophisticated robotic systems that are revolutionizing the landscape of textile factories. These robotic systems are not merely replacing human labor; they are augmenting human capabilities, enhancing precision, and propelling the industry towards new heights of efficiency and productivity.
Precision at Every Stage: From Fiber to Finished Product: Robotic systems are transforming every stage of textile production, from fiber preparation to garment assembly. In fiber preparation, robots handle delicate fibers with precision, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing waste. In spinning, robots precisely control yarn formation, producing consistently strong and uniform threads.
In weaving and knitting, robots seamlessly interlace fibers to create fabrics with intricate patterns and textures. In dyeing and finishing, robots apply chemicals and treatments with precision, ensuring uniform color and consistent quality. In garment assembly, robots perform tasks like cutting, sewing, and finishing with remarkable dexterity, producing garments with precise fit and high-quality stitching.
Enhanced Productivity: Speed and Efficiency in Harmony: Robotic systems not only enhance precision but also significantly boost productivity. They operate tirelessly, working 24/7 without breaks, ensuring continuous production and minimizing downtime. Their speed and accuracy surpass human capabilities, leading to increased output and accelerated production cycles.
Robots also contribute to productivity by reducing errors and minimizing waste. Their precise movements and consistent performance reduce defects, leading to fewer rejects and higher yields. Additionally, robots can optimize material usage and minimize waste during cutting and sewing processes, further enhancing overall efficiency.
A Collaborative Workforce: Humans and Robots Working in Tandem: The integration of robotics into textile factories does not herald the replacement of human workers; it rather paves the way for a more collaborative and productive workforce. Robots take over repetitive and physically demanding tasks, allowing human workers to focus on higher-value activities such as design, quality control, and customer service.
This human-robot collaboration fosters a synergistic environment where the strengths of both are combined. Human workers provide their expertise, creativity, and problem-solving abilities, while robots contribute their precision, speed, and tireless work ethic. This collaboration leads to improved decision-making, enhanced innovation, and a more efficient and productive work environment.
A Sustainable Future: Robotics for Environmental Responsibility: The textile industry faces increasing scrutiny for its environmental impact. Robotic systems offer a promising path towards sustainable textile production. Their precision and efficiency reduce waste and minimize the consumption of energy and resources. Additionally, robots can be programmed to optimize material usage and minimize energy consumption during production processes.
Moreover, robotic systems can be adapted to handle recycled materials and incorporate sustainable practices into the production cycle. This commitment to sustainability not only reduces the environmental footprint of textile manufacturing but also aligns with the growing demand for eco-conscious products.
The Role of IoT in Textiles: Revolutionizing the Supply Chain, Quality Control, and Streamlining Processes
The textile industry, a global pillar of manufacturing and innovation, is undergoing a transformative journey fueled by the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT, the interconnected network of devices embedded with sensors and software, is revolutionizing every aspect of the textile supply chain, from raw material sourcing to finished product delivery. This technological revolution is optimizing operations, enhancing quality control, and streamlining processes, leading to unprecedented levels of efficiency, transparency, and sustainability.
Optimizing the Supply Chain: A Connected Network for Seamless Operations: IoT is transforming the textile supply chain into a hyperconnected ecosystem, enabling seamless data exchange and real-time visibility. Sensors embedded in raw materials, machinery, and transportation vehicles provide continuous data streams, tracking the movement of goods from farm to factory to consumer. This real-time visibility empowers manufacturers to optimize inventory management, anticipate supply chain disruptions, and make informed decisions to ensure timely delivery and minimize disruptions.
For instance, IoT-enabled sensors can monitor the environmental conditions during fiber cultivation, providing valuable insights into crop health and yield predictions. This data can inform farmers on irrigation and fertilizer needs, optimizing resource utilization and enhancing crop quality.
Ensuring Quality Control: A Network of Vigilant Guardians: IoT is playing a pivotal role in ensuring textile quality control, preventing defects, and maintaining consistency. Sensors embedded in manufacturing equipment monitor critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and yarn tension, providing real-time feedback to production lines. This real-time data enables proactive interventions, preventing defects before they occur and ensuring that products meet stringent quality standards.
For example, IoT-enabled sensors can monitor the spinning process, detecting subtle changes in yarn tension that could lead to unevenness or breakage. This real-time feedback allows operators to adjust machine settings and prevent defects before they occur.
Streamlining Processes: Automation and Efficiency at Every Stage: IoT is streamlining processes across the textile value chain, automating repetitive tasks, and optimizing resource utilization. IoT-enabled devices can automate tasks such as material handling, sorting, and packaging, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. Additionally, IoT can optimize energy consumption by monitoring and controlling machine performance, reducing energy usage and minimizing environmental impact.
[Image of IoT-automated processes in textile industry]
For instance, IoT-enabled sensors can monitor the energy consumption of textile machinery, identifying areas where energy usage can be optimized. This data can inform energy-saving strategies, reducing costs and environmental footprint.
The Future of IoT in Textiles: A Vision of Connected and Intelligent Manufacturing: The future of IoT in textiles is filled with exciting possibilities, promising to revolutionize the industry even further. As IoT technology continues to advance, we can envision a future where textile manufacturing is fully connected and intelligent, with seamless data exchange, real-time decision-making, and predictive maintenance.
IoT will enable manufacturers to optimize production processes based on demand fluctuations, minimize waste through predictive maintenance, and personalize products based on individual preferences. This connected and intelligent manufacturing will lead to a more sustainable, efficient, and responsive textile industry, shaping the future of fashion and beyond.
Conclusion
The textile industry’s journey from manual labor to high-tech innovation is marked by remarkable advancements. Fueled by technologies like AI, robotics, and blockchain, the industry has undergone a dynamic transformation across the entire value chain, enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
These cutting-edge technologies aren’t replacing humans but augmenting their capabilities, fostering collaboration and productivity. Beyond the factory, augmented reality is reshaping the shopping experience, and 3D printing is revolutionizing textile design and production.
Looking ahead, the future of textiles holds exciting possibilities. With the convergence of technologies and a focus on sustainability, textiles will become integral components of our lives, adapting to our needs and enhancing well-being. From personalized clothing to smart textiles monitoring health, the textile industry is set to pioneer innovation and human-centric design.
In this future, textiles will be smarter, more sustainable, and seamlessly integrated into daily routines. Embracing technology and ethical practices, the textile industry is poised to express creativity, values, and a deep connection to the world.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.